Three Dimensional Shapes (3D Shapes)
Updated on November 28, 2025
All around us are three-dimensional shapes — from toys to buildings to boxes to food. At Brighterly, we transform everyday objects into fun learning experiences that empower kids. In this article, we will explore the properties, applications, and importance of 3D shapes in geometry. You’ll also discover how recognizing 3D shapes builds spatial reasoning skills and boosts confidence in problem-solving. These foundations help kids navigate both classroom tasks and real-world challenges with ease.
What are three dimensional shapes?
The term 3 dimensional shapes refers to objects with length, width, and height. A 3D shape occupies space in the real world, unlike a two-dimensional shape, which is flat and has only two dimensions. Many fields, including architecture, engineering, and design, rely heavily on geometric shapes.
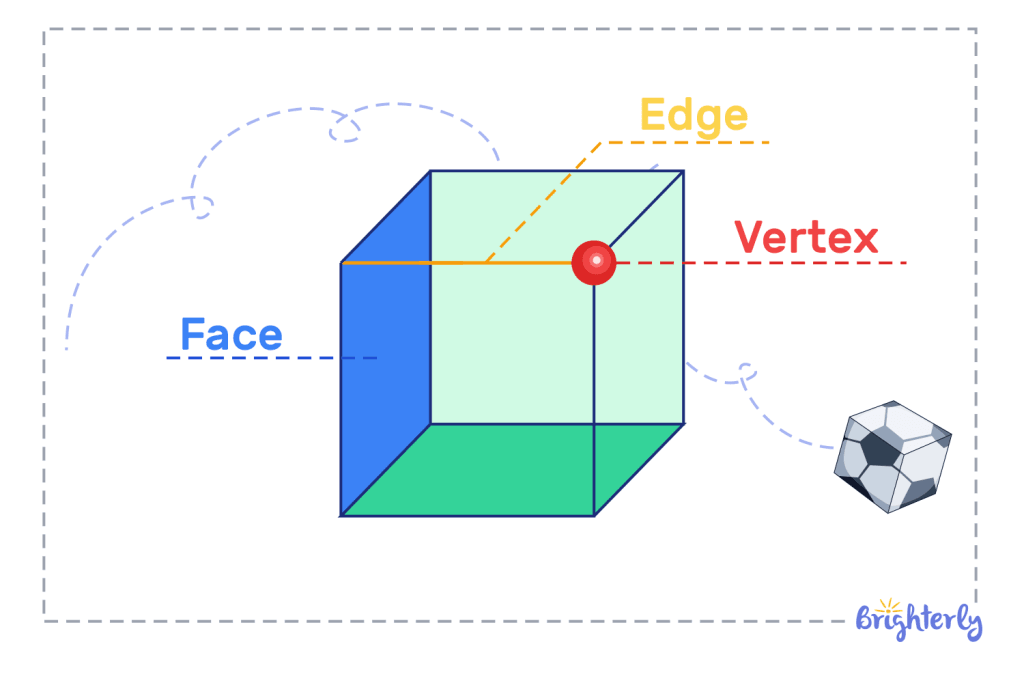
Faces, edges, and vertices of three dimensional shapes
There are three primary components to shapes 3D, faces, edges, and vertices:
- Faces are flat surfaces,
- Edges are lines where two faces meet
- Vertices are points where three or more edges meet.
List of three dimensional shapes
Three dimensional shapes are many and varied. Here are just a few to list:
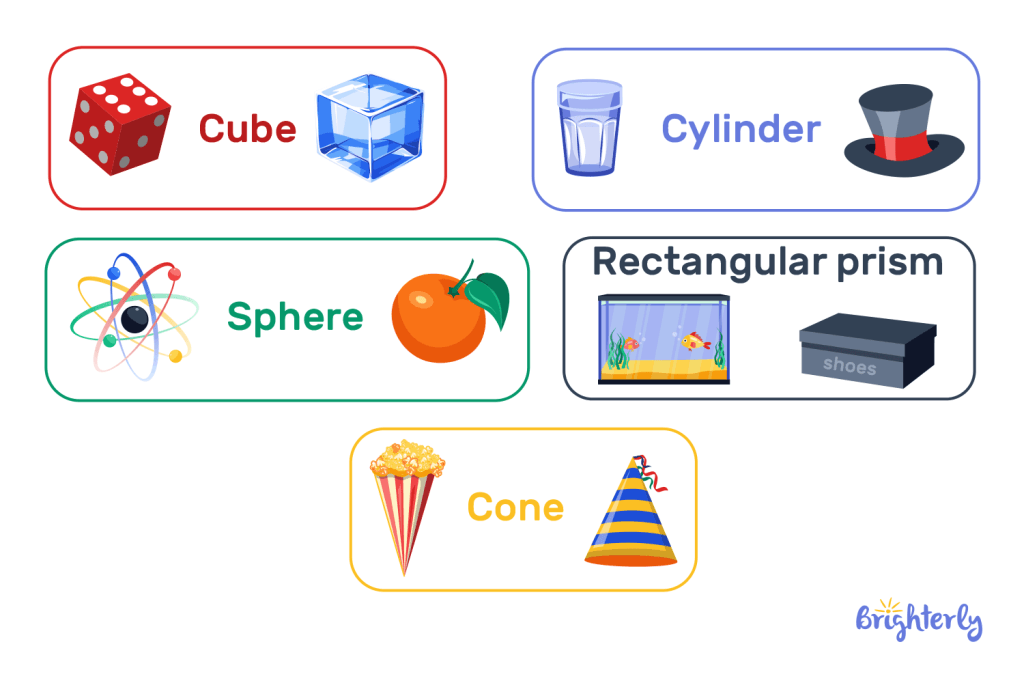
Cube
Each of the cube’s eight vertices connects three of its twelve edges. Each cube face is perpendicular to the others, and each angle is right-angled. Cubes are found in many everyday objects, such as building blocks, dice, and Rubik’s cubes.
Learning about cubes is a great way for children to become familiar with names of 3D shapes and their properties. They also help kids understand symmetry, measurement, and how objects fit together in space.
Cuboid
They make a stable, well-organized figure with six rectangular faces and twelve edges. Cuboids are useful and adaptable because their rectangular faces can be customized according to the environment. Books, bricks, and shoeboxes are everyday items that illustrate how cuboids are found in our environment.
As a concrete way to learn three-dimensional shapes, cuboids allow children to visualize edges, faces, and vertices. Moreover, they help children understand concepts such as surface area, volume, and how dimensions influence overall shape.
Prism
As polygons can be shaped in any way, prisms can take any shape — triangles, rectangles, hexagons, and more. Their rectangular sides connect two parallel, matching bases. The shape of Toblerone bars is triangular, and the shape of wooden pencils is hexagonal. These real examples of 3D shapes in prisms provide an excellent illustration of how volumes and surface areas are measured.
Pyramid
The apex of a pyramid is the point at which all the triangular faces meet. Also, pyramids come in different types as determined by their base shapes. Some of the most common examples include triangles, squares, pentagons, etc. But this 3D form appears not only in history and architecture but also in toys, art projects, and everyday stacked objects.
Cylinder
Every day, we come into contact with cylinders. The two bases are circular and are connected by a smooth, curved surface. Using the circles as a guide, measure the distance between them to determine the cylinder’s height. In the real world, kids can learn about cylinders by comparing soda cans, glue sticks, water pipes, and building columns.
Cylinders are a great way to introduce children to the concept of a 3D circle name and how flat shapes can form solid objects. Observing cylinders in everyday life helps kids connect geometry to the world around them and understand volume and height.
Cone
A cone begins wide at the bottom and narrows to a single sharp point at the top, making it one of the simplest 3D figures to recognize. It has a circular base and a smooth, curved surface that wraps upward to the apex. It’s everywhere. Ice-cream cones, traffic cones, party hats, and even nature’s pinecones all have cones on them. It helps children understand how flat circles become tall, pointed solids.
Sphere
There is no better shape in 3D figures than a sphere. Each spot on its surface is the same distance from the center, giving it a smooth, even shape without edges or corners. In real life, spheres are everywhere: balls, marbles, bubbles, fruits, planets, and even raindrops. With their simple, balanced shapes, kids can connect geometry to everyday objects.
3d shapes for kids: Importance
The world is filled with objects that have their own 3D shapes names. These are toys, buildings, boxes, and balls, to name a few. Kids are naturally drawn to three-dimensional shapes when they learn about them. Besides, when children explore 3D shape attributes, like faces, edges, and vertices, they build spatial reasoning skills that help with math, engineering thinking, and everyday problem-solving.
Additionally, this subject fosters creativity. Children begin to understand how shapes come together to form larger objects; this is a skill that can be applied to drawing, crafting, building with blocks, and even simple game coding. It gets easier to comprehend measurements, symmetry, and how objects fit together in space the more they work with 3D shapes.
Conclusion of 3D shapes
Exploring different 3D shapes helps children see that geometry isn’t just something in textbooks — it’s all around them. Brighterly transforms these discoveries into meaningful learning experiences that pique curiosity and cultivate a lifelong love of math through straightforward, relatable examples. Each 3D shape is unique, with its own properties and features, offering countless ways to explore and understand the world.
By learning about these shapes, children strengthen their spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills. Understanding all 3D shapes is also key to grasping more advanced math concepts and real-world applications in fields like engineering, architecture, and design, where shapes are essential in creating and building structures.
Frequently asked questions of three dimensional shapes
What is 3D?
3D refers to an object which obtains all three properties: length, width, and height. 3D objects occupy space and can be viewed from various perspectives, unlike flat 2D shapes. Cones, balls, and boxes are examples of commonplace 3D geometric shapes with actual volume.
What is a three dimensional shape?
A three dimensional shape is one that has length, width, and height. Because they are not flat, they can be grasped or touched. Cubes, spheres, cylinders, and cones are some examples.
What are the attributes of 3D shapes?
3D shapes have specific attributes such as faces (flat or curved surfaces), edges (lines where faces meet), and vertices (corners). These attributes help describe how the shape looks and behaves. Different types of 3D shapes have different combinations of these parts.
What are the main components of a 3D shape?
There are three main components in three-dimensional shapes: faces, edges, and vertices. Vertices mark the point where edges meet, faces can be flat or curved, and edges connect two faces.
What are the top 3D shapes examples?
The top 3D geometric shapes are a cube (like a dice), a sphere (like a ball), a cylinder (like a can), a cone (like a cone of ice cream), and a pyramid (like the Great Pyramid). Objects like these help children understand and recognize three-dimensional shapes.