Acute Angle – Definition, Types, Examples
Updated on December 1, 2025
At Brighterly, we want kids to see that math isn’t just something in a textbook. One of the easiest places to start is by learning about acute angles. When kids learn the acute angle definition geometry uses, they begin to notice how often these angles appear in drawings, patterns, and even in nature. With this simple concept, they build confidence and prepare for more advanced topics in geometry.
What is an acute angle?
Any angle that is smaller than ninety degrees is considered acute. These angles are a crucial component of geometry because they appear in everything from triangles to architectural designs.
To build students’ confidence, we at Brighterly present these concepts in a simple, kid-friendly way. Use our math worksheets to make the subject easy and enjoyable, to develop strong skills.
Lines and Angles Worksheets
Types Of Angles Worksheets
Definition of an acute angle
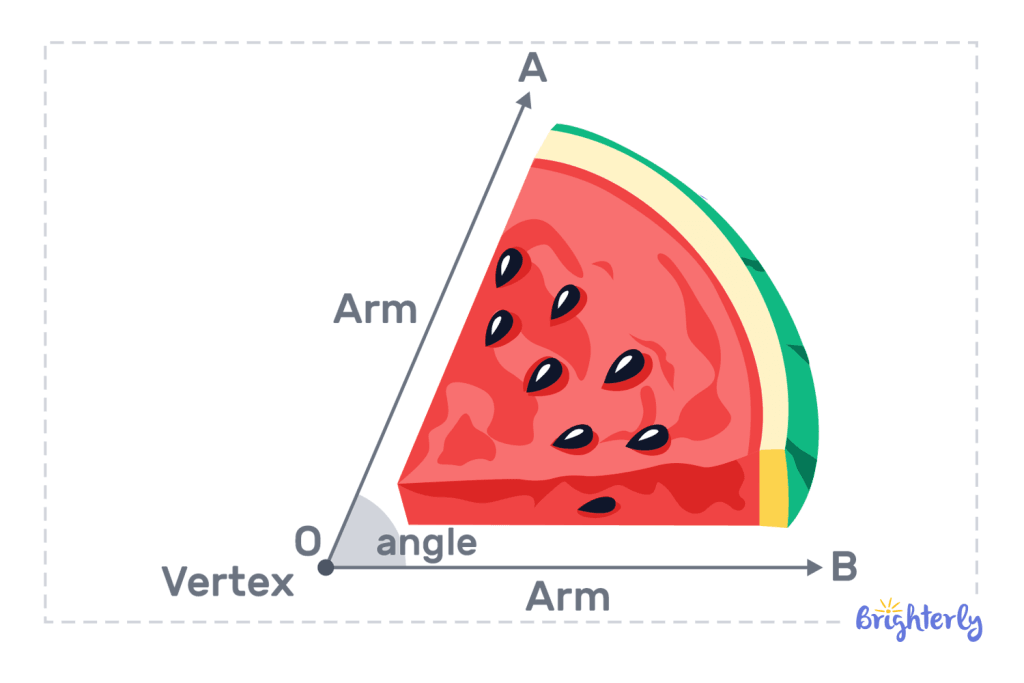
In geometry, an acute angle definition is simple — it is an angle that is greater than 0° but less than 90°. This kind of angle, which is smaller than a right angle, is formed when two lines or rays come together at a point known as the vertex.
Acute angle degree
We can measure the degree of an angle by how wide or narrow it is. Circular shapes have 360 degrees, and acute angles have 0° to 90°. Due to its clear difference from 90 degrees, a 45° angle is a perfect example of an acute angle shape.
Acute angle formula
There isn’t a special formula for finding an acute angle — the main idea is simply understanding what degree is an acute angle. Any angle smaller than 90° fits this category. But you can calculate a missing acute angle when working with triangles.
For this, you need to use the angle-sum rule. Since all triangle angles add up to 180°, you just add the two angles you already know and subtract that total from 180°. This is a quick and reliable way to figure out the third angle.
Types of angles
Knowing facts about acute angles and others helps you to understand the differences between angles and recognize them in everyday life:
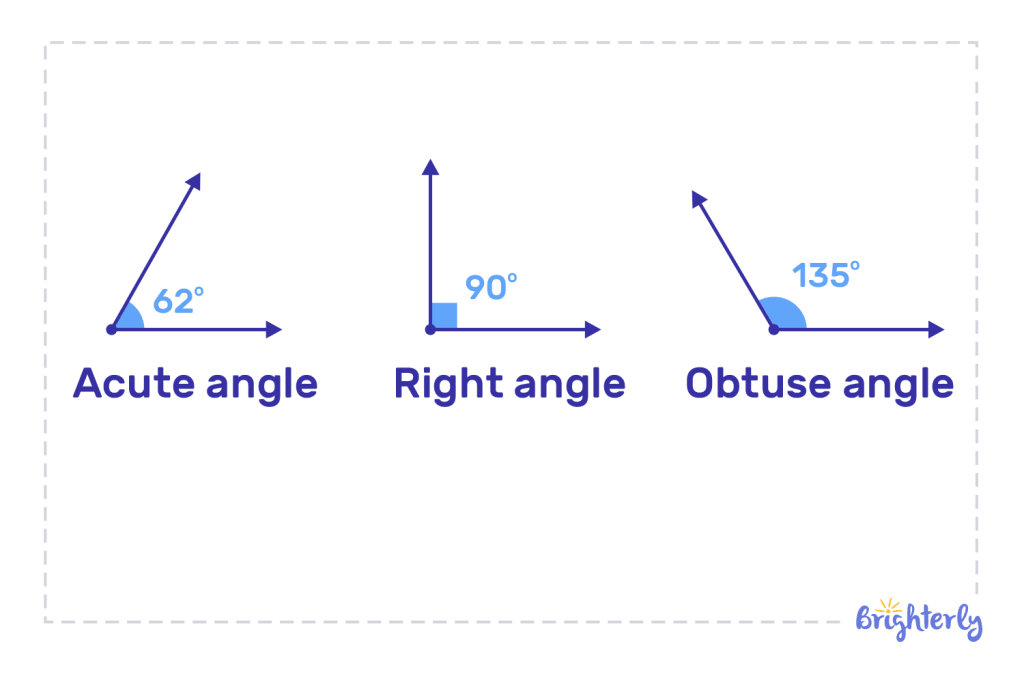
- Angles less than 90° are called acute angles.
- A right angle is one that measures exactly 90 degrees.
- An obtuse angle is one that is greater than 90° but less than 180°.
- The straight angle measures exactly 180°.
Acute angle triangle
Triangles with acute angles have three interior angles. In other words, every angle in the triangle is less than 90°, which gives it a sense of sharpness and balance. You’ll see this triangle type all the time in geometry and in everyday shapes like mountain peaks, arrows, and roof designs.
Acute angle triangle properties
Triangles with acute angles have the following properties:
- According to the Triangle Inequality Theorem, any square of the lengths of two sides is greater than the square of the length of the third side.
- In a triangle, the largest side is opposite the smallest angle.
- Located within the triangle is the circumcenter (the point where the two perpendicular bisectors meet).
- The incenter of the triangle is also the intersection of the angle bisectors.
Acute angle parallelogram
A parallelogram cannot have only acute angles. In any parallelogram, opposite angles are equal, and each pair of adjacent angles must add up to 180 degrees. Because of this, if one angle is acute, the adjacent one must be obtuse. Therefore, a parallelogram made up entirely of acute angles cannot exist in geometry or in real life.
Acute angle trapezoid
A trapezoid with acute angles has at least one pair of angles that are less than 90°. Trapezoids always have one pair of parallel sides, and their angles can differ. If one or both non-parallel sides form acute angles with the parallel sides, the trapezoid is called an acute-angle trapezoid.
Real life examples of acute angles
The sharp, narrow angles appear both naturally and in man-made designs. Here are some simple acute angle examples in real life:
- The angle at the tip of a triangular road sign.
- The angle between the hands of a clock when the time is around 10:00–11:00.
- The angle made by a folded piece of paper in origami.
- The shapes with acute angles are on a ramp leading to the ground on a small playground slide.
Examples of acute angles
An acute angle can be described as follows:
- At 1:00, the hour and minute hands of a clock form an angle of 30°.
- A diagonal of a square or rectangle forms a 45° angle.
- A triangle with equilateral sides and equal angles has a 60° angle.
Solved examples on acute angles
Here are a few simple examples to help students better recognize an acute angle in real life:
Example 1
Question: An angle measures 35°. Is it an acute angle?
Solution: Acute angles must be greater than 0° and less than 90°. Since 35° fits this range, it is an acute angle.
Answer:
| Yes, it is an acute angle. |
Example 2
Question: One angle in a triangle is 50°, and another is 60°. Find the third angle.
Solution: Use the angle sum of a triangle:
50° + 60° = 110°
180° − 110° = 70°
Since 70° is less than 90°, the third angle is acute.
Answer:
| The third angle is 70°. |
Practice problems on acute angles
Take a look at these problems and see if you can solve them:
- 47° is a measure of an angle. Is it acute or not?
- There are two angles in a triangle: 40° and 55°. Do you know the measure and the angle of the third angle?
Conclusion
Identifying an acute angle example is simple since acute angles are any angle less than 90°. Once your child can identify these angles, they are prepared for more advanced concepts and gain greater confidence in learning math.
Frequently asked questions on acute angle
What are acute angles?
An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90 degrees.
What are some examples of acute angles?
Examples of acute angles include the tip of a slice of pizza, the peak of a roof, the point of a pencil, the corner of a folded paper, and slightly opened scissors.
What shape has all acute angles?
A shape with all acute angles is a triangle, where all three angles are less than 90 degrees. All angles are acute, making this shape a perfect example of shapes with acute angles.
How many acute angles are in an acute triangle?
An acute triangle has three acute angles, each measuring less than 90 degrees.
Can a parallelogram have all acute angles?
No, a parallelogram cannot have all acute angles because its opposite angles are equal, and the sum of adjacent angles is 180 degrees.