Prime Numbers – Definition with Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on January 6, 2026
At Brighterly, we believe that every child can master math when complex ideas are explained simply and step-by-step. Prime numbers are one of those concepts that may look confusing. But with the right approach, kids quickly see how important and fascinating they are.
Prime numbers appear not only in arithmetic or algebra, but even in the technology we use every day. That’s why understanding what makes a number “prime” is important. We break the topic down into clear explanations, add example of prime numbers, and easy methods to understand how they work.
What are prime numbers?
Speaking of what prime numbers are, it’s safe to say that it’s a natural number more than 1 that has no divisors other than 1 and itself. In other words, a prime meaning in math is that this number cannot be exactly divided by any whole number except for 1 and itself.
Prime number definition
The definition of prime number states that it’s a number that can be evenly divided only by 1 and itself.
For better understanding it’s great to look on prime number definition with example. For instance, you can divide 4 in multiple ways: by 1, by 4, and as the sum of two 2 (since 2 x 2 = 4). It means that 4 can’t be the prime number.
But 5 equally divides only by 1 and by 5. In other cases, we won’t get a whole number. If we try to divide 5 by 2 (5 ÷ 2), we will get a 2.5, which can be counted as a decimal fraction or rational number 5/2. But it’s still not a whole number! So, 5 will count as the prime number as we can divide it by 1 and by itself to get a whole number as the result.
The smallest prime number is 2, as you can divide it only by 1 (as 2 ÷ 1 = 2) or by itself (2 ÷ 2 = 1).
Prime number examples
2, 3, 5, 7, 11,13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97. These are all prime numbers under 100. All other numbers have at least an additional way to divide and get a whole number as a result.
What are all the prime numbers?
Since every prime number goes on infinitely, there is no complete list. However, mathematicians have identified primes within certain ranges to help learners recognize patterns and understand how primes behave. So, let’s explore what are the prime numbers?
Below are some commonly referenced sets of prime numbers:
- Prime numbers under 50:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47 - Prime numbers under 100:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97 - Prime numbers under 200:
101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199
This list shows how prime numbers appear less frequently as numbers grow larger, but they never completely stop. That’s why primes are often called the “building blocks” of all natural numbers — every number can be broken down into a product of primes.
Properties of prime numbers
Prime numbers have several recognizable properties. Let’s examine them in detail.

Prime numbers chart
A prime numbers chart, or Eratosthenes chart, is a numerical prime number table that records all prime numbers and prime factors.
A chart of prime numbers is one of the quickest ways of identifying those numbers. It comes with prime numbers already determined and arranged in rows and columns, with the prime numbers highlighted.
The prime numbers chart gives you a quick reference for identifying specific numbers. It can also teach concepts related to prime numbers, such as factorization and divisibility. It even helps with pattern recognition, as when students define a prime number, they can visualize patterns and sequences, leading to further exploration and discovery.
Easy ways to find prime numbers
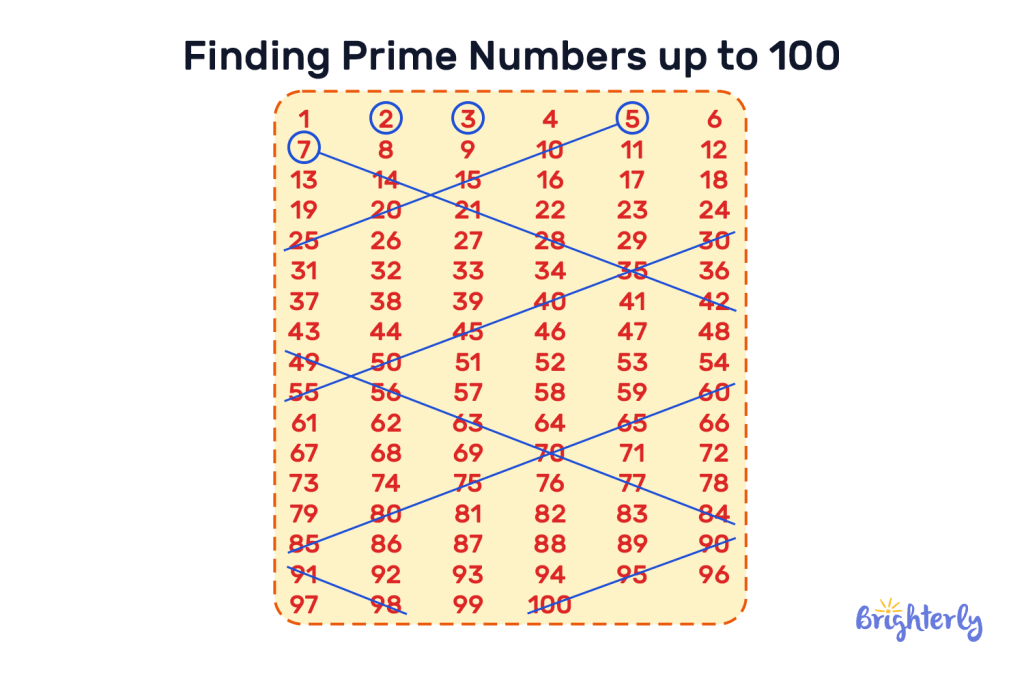
There are many ways to find prime numbers, but most of them are complicated. The easiest way is called the Sieve of Eratosthenes. Here we showcase how to easily find prime numbers 1 to 100, but you can use it even with larger numbers:
- Create a list of consecutive integers from 2 to the given limit.
- Mark the first number (2) as prime.
- Cross out all multiples of 2 (starting from 4, every second number).
- Find the next unmarked number (3), and mark it as prime.
- Cross out all multiples of 3 (starting from 6, every third number).
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 for the next unmarked number (5, 7, etc.) until the square root of the limit is reached.
- The remaining unmarked numbers are prime.
This scheme perfectly works with prime numbers 1-100. After that, it becomes more complicated, but still works well.
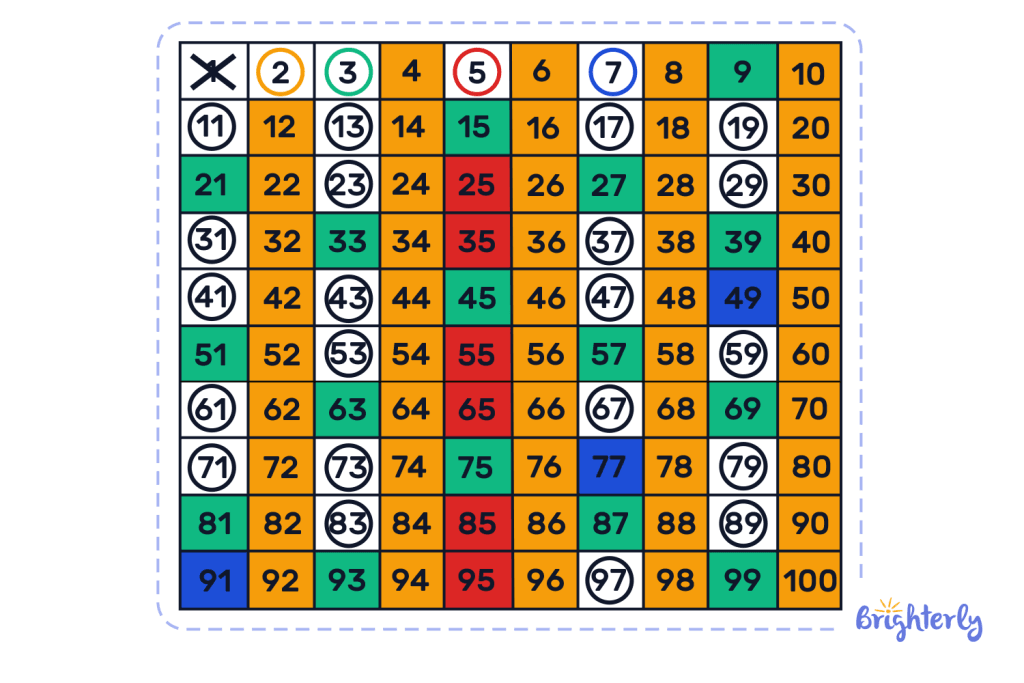
Prime factorization
Another relatively easy way to determine numbers that are prime is to use the prime factorization method. The operating principle is similar to Eratosthenes’ Sieve, but with minor changes:
- Divide the number into factors.
- Check how many factors that number has. If the number of factors is more than 2, then it is composite. For instance, 8 has four factors: 1,2,4 and 8. So we can state that it’s not a prime.
- All prime numbers greater than 3 can be represented by the formula 6n+1 and \(6n -1) for n greater than equal to 1. Exception if the number ends with 5 or higher multiples of 7, such as 49, 77, 91. For instance, 5=6×1−1, 7=6×1+1, 11=6×2−1, 13=6×2+1.
In this case, a chart of prime numbers 1-100 will look like the next illustration.
List of prime numbers
While there is no complete list of all prime numbers, as there is an endless amount of options, we can help you with the most common variants.
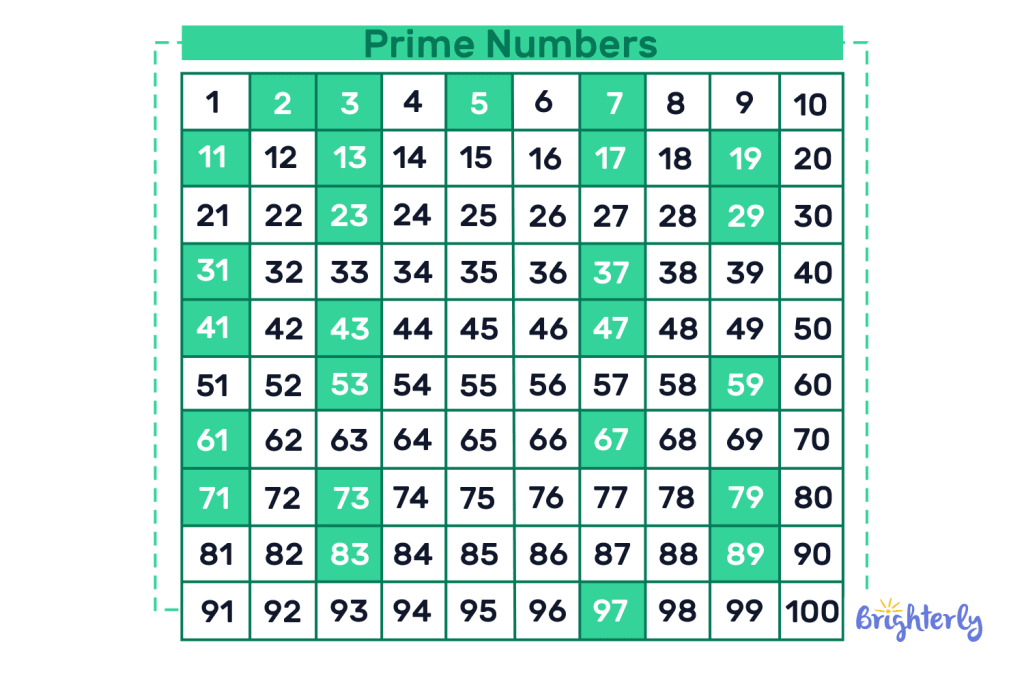
List of prime numbers 1 to 100
Speaking of how many prime numbers are between 1 and 100, there are only 25 numbers on this list. It’s also include all prime numbers between 1 and 10. You can see them in the picture below.

The lowest prime number is 2.
List of prime numbers 1 and 200
Between 1 and 200, there are 46 prime numbers list. You can see prime numbers up to 200 in the picture below.

Prime numbers between 1 and 1000
If you are interested in the prime numbers between 1 and 1000, there are 168 numbers on the list. You can see prime number chart 1-100 in the picture below.

Prime numbers and composite numbers
Many features differentiate a prime number from a composite number. A prime number definition states it is a natural number greater than 1 with just two factors. Meanwhile, composite numbers are greater than 1 with more than two factors. So, they can be easily divisible by more than two factors.
Speaking of prime numbers 1-6, number 1 is neither; 2 is the only even prime number. 3 and 5 are prime. Meanwhile, 4 and 6 are composite since they can be divided in more than two ways.
Prime number chart
A prime number chart to 100 is relatively easy since it works with the Sieve of Eratosthenes and prime numbers.
Prime numbers worksheets
A prime number meaning is simple and simultaneously so complex, even for adults. That’s why we created free prime number sheet that can help you boost your knowledge and skills:
Solved examples of prime numbers
To solidify your knowledge, we want to practice some solved examples of prime numbers with you.
Solved math example 1
We have numbers from 1 to 25. Which of these numbers is prime? Why?
Answer
The prime numbers from 1 to 25 are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19 and 23.
| A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. |
Solved math example 2
Imagine that you see a line of numbers from 130 to 175. Which of the following numbers are prime? How do you determine prime numbers if they are larger than 100?
Answer
| The prime numbers between 130 and 175 are 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163 and 167. |
Use the Sieve of Eratosthenes and prime numbers to define a prime number. They still work even with numbers larger than 100.
Prime Numbers: Practice Math Problems
Frequently Asked Questions on the Prime Number
Is 1 a prime number?
No. Even though 1 seems like it could be prime, it isn’t. A prime number must have two positive divisors. But 1 can only be divided by… 1. So it doesn’t qualify.
Can a prime number be negative?
No. Prime numbers are always positive and start from 2. Negative numbers don’t fit the definition because primes must have exactly two positive divisors.
What is the difference between a prime number and a co-prime number?
The main difference between a prime number and a co-prime number is that a prime number is a single number with no divisors except 1 and itself; at the same time, Co-prime numbers are two numbers that don’t share any common factors.
What is the smallest prime number?
2 is the smallest prime number, as it has only itself and 1 as the divisors.
What is the largest known prime number?
The largest known prime is a huge Mersenne prime discovered in 2018. It has over 24 million digits — far too big to write out. It was found by GIMPS, a global network of computers searching for even bigger primes.
Which numbers are not prime numbers?
Any natural number greater than 1 that can be divided by 1, itself, and any other number is not a prime number. For instance, 4 can be divided by 1,2 and 4. So, we can’t count 4 as a prime number.







