Slope – Types, Definition With Examples
Updated on November 28, 2025
When it comes to algebra and geometry, the slope is an integral part of your learning.
It’s a key tool in both math and the real world. That’s because we use it to calculate real-world values, such as stock market movements and speeds. Thus, mastering this concept in math class offers you a range of benefits beyond the classroom, too!
Here, we’re going to cover everything you need to know about the slope. We define slope, cover the different slope types and their properties, and write equations with slopes. Then we’ll share practice problems so you can test your understanding of this concept.
What is slope?
A slope, both in math and real life, is a numerical measure of how steep a line is and whether it increases or decreases as it moves left to right. It essentially tells us how much a line rises or falls on its journey. We cover the full slope definition below.
Definition of slope
The definition of slope in math is the vertical change (also known as the rise) of a line per unit of horizontal change (also known as the run). We record this as a ratio, which represents the vertical change from one point to another on a coordinate plane and yields a numerical value.
Types of slopes
Now that we’ve covered the slope definition math, let’s explore the different types of slope.
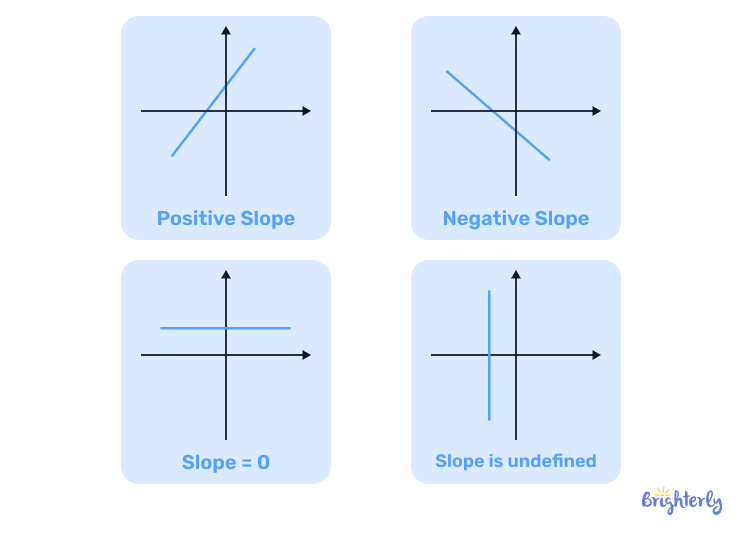
Positive slope
A positive slope is a line that moves in an upward trajectory from left to right, meaning its endpoint will be higher than its starting point. This kind of slope generally represents a positive relationship between two variables.
Negative slope
A negative slope is a line that moves in a downward trajectory from left to right, so its endpoint will be lower than its starting point. This usually means there is a negative (or inverse) relationship between two variables.
Zero slope
A zero slope line is a straight, horizontal line that does not move upwards or downwards as it goes across your coordinate plane. As the x-coordinate increases, the y-coordinate does not.
Undefined slope
An undefined slope is a straight, vertical line that does not move left or right as it goes across your coordinate plane. We cannot calculate the slope, because the change in x is 0, so it’s considered undefined.
Properties of different types of slopes
All different slopes on a graph have unique properties that make them different from other slopes. Let’s take a look at those properties!
Properties of positive slopes
- Positive slopes always move upward from left to right
- The steeper the slope, the faster the line rises
- Positive slopes represent a positive relationship between your two variables, meaning that as one rises, the other does too
Properties of negative slopes
- Negative slopes always move downward from left to right
- The steeper the slope, the faster the line drops
- A negative slope means that as x increases, y decreases
Properties of zero slopes
- A zero slope line is a horizontal line that does not change in steepness
- It represents no change in your dependent variable (y), no matter how much your independent variable (x) changes
- The equation of a zero slope is consistent and always written as y = b
Properties of undefined slopes
- Undefined slopes are vertical lines that do not move left or right on your coordinate plane
- It represents no change in your independent variable (x), while your dependent variable changes (y)
- It is always defined by the equation x = a
The difference between different slopes
The difference between our different types of slope line is whether they move upwards or downwards, or whether they move horizontally or vertically at all. Positive and negative slopes can be considered opposites, as one moves up and one moves down. Zero and undefined slopes, meanwhile, are opposites as one is a flat horizontal line and the other is a flat vertical line.
Slope examples
Now that you know what is slope in math, it’s time to move to practice. There are many examples of slopes around us in real life, and understanding how they move up and down can help us understand how they operate in math. Here are just a few examples to keep in mind:
- A steep hill represents a positive slope on one side, and a negative slope on the other side
- The side of a building is an undefined slope example
- A flat path is an example of a zero slope
Slope equations
All slopes are defined by equations, so it’s important to understand them when it comes to graphing and marking slopes. There are two key slope equations that you’ll use in math class.
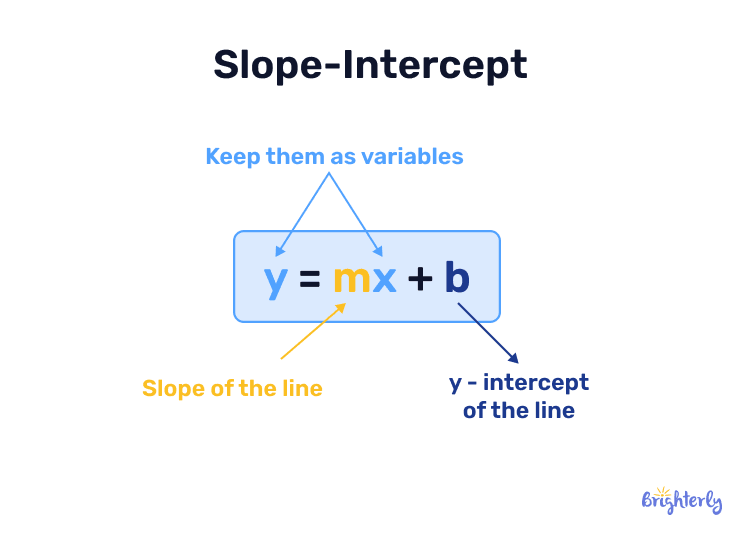
Slope-intercept form
The slope-intercept form is the equation of a line slope, and is represented by y = mx + b. In this equation, m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept. This formula is commonly used because it’s easy to read and interpret.
Point-slope form
If we know the slope of our line and a point on it, we can use the point-slope form. This is represented by y – y1 = m(x – x1). Here, m represents the slope once again, while x1 and y1 are our x and y coordinates.
Writing equations using slopes
In geometry and algebra class, you’ll be required to write equations using slopes, so here’s how you do that with each type of slope.
Writing equations with positive slope
Use the y = mx + b formula to write equations with a positive slope. To ensure it’s a positive slope, you’ll need to check that m has a positive value, which shows that it moves upwards. A positive slope equation example is y = 2x + 3.
Writing equations with negative slope
When writing equations for negative slopes using y = mx + b, the opposite is true. Your m value must be negative to represent a downward slope. An example of a negative slope equation is y = -2x + 3.
Writing equations with zero slope
Because the value of m is always 0 in equations for zero slope, you can simply represent it as its y-coordinate. An example of a zero slope equation is y = 3.
Writing equations with undefined slope
For an undefined slope, the slope value does not exist. Vertical lines cannot be written in slope-intercept form, so their equations are written as x = a.
Practice problems on slope in math
Now it’s time to put your newfound knowledge on slopes to the test! These practice questions can help you familiarize yourself with the types of questions you’ll come across in math class and school exams.
- You have the equation y = 2x + 3 for a positive slope. If x is 4, what is y?
- You have the equation y = -3x + 1 for a negative slope. If x is 2, what is y?
- You have the equation y = 5, what would be the y value when x is any number like 7, 10, or 100?
- You have the equation x = 4. List some possible coordinates of a point on the line.
Conclusion on types of slopes
Here, we’ve covered the slope definition, the four different types of slopes, their properties, and equations. Now, you can be confident in identifying and working out any slope you come across! For more learning details on slopes, check out our types of slope worksheet.
Frequently asked questions on slopes
What is a slope?
Slope is a line that is measured in its steepness, aka how much it rises or falls, as it moves side to side across a coordinate plane. We can have positive, negative, horizontal, and vertical slopes. This is the complete meaning of slope in math.
How many types of slopes are there?
There are four types of slopes:
- Positive slope: Moves upwards across your coordinate plane
- Negative slope: Moves downwards across your coordinate plane
- Zero slope: A horizontal line that doesn’t move up or down
- Undefined slope: A vertical line that doesn’t move left or right
How to find the slope of a line?
If you have a line on a graph, you can find the slope by using the formula m = rise ÷ run. You can also calculate it by working out how many units on the y-axis your line moves per unit on the x-axis.
What does a steeper slope represent?
A steeper slope represents a stronger relationship between your two variables and a greater rate of change. If you have a positive slope, this represents a sharp increase, while a negative slope represents a sharp decline.
Why is the slope of a vertical line undefined?
The slope of a vertical line is undefined because, to work out the slope of a line, you must divide the rise by the run. Because the run is always 0 in a vertical line, it is impossible to divide by that. Therefore, your slope is undefined.






