Algorithm in Math – Definition with Examples
Updated on November 3, 2025
Are you ready for another exciting journey through math with Brighterly?
We explore all types of math concepts, from operations to geometry, to give you all the knowledge you need to become a math whizz. Today, we’re going to be diving into one of the most fundamental elements of math to exist: the algorithm in mathematics.
Here, we’re going to look at the algorithm definition math, their properties and different types of algorithms. We’ll also explore different equations and formulations and provide algorithm examples for students. Finally, we’ll share some practice questions for you to test yourself out on, and answer some commonly asked questions on the algorithm.
What are algorithms in math?
Algorithms form the foundation of math. They are step-by-step processes that allow you to solve many different types of problems and puzzles. Algorithms can be applied to many areas of science and math, including algebra, calculus, geometry and statistics.
You might not know that items we use in our everyday lives are powered by algorithms. Car and phone GPS systems use algorithms, while what you see on your social media feeds is also dictated by an algorithm. They’re everywhere!
We explore the full definition of a math algorithm below.
Definition of an algorithm
The definition of an algorithm is a sequence of instructions that allow you to solve a problem. You will have a finite number of precise steps to take in order to accomplish your task, and they are unmoving, so you must complete them exactly as instructed.
Algorithms are often used by computers for a range of tasks, but we can consider simple steps to solve a basic math calculation an algorithm too.
Algorithm math example – subtraction steps:
- Identify your two numbers
- Take one away from the other — you could do this by counting backwards on a number line
- Write down your final answer
Properties of algorithms
There are some properties of algorithms that always apply. So, what is a mathematical property of an algorithm?
- Definiteness: Each step in an algorithm must be clearly defined and unambiguous
- Finiteness: An algorithm must have a set number of steps and should not get stuck in an infinite loop
- Effectiveness: The algorithm should achieve what it sets out to achieve
- Input and output: The input (data, instructions etc.) and the output (result) must be clearly defined
- Feasibility: The algorithm should be able to achieve what it is designed to achieve
- Language independence: Algorithms should be useable in different languages
Types of algorithms in mathematics
In mathematics, there are different types of algorithms that are defined by their structure and/or purpose. Here are some key types of mathematical algorithms based on their structure:
- Sequential algorithms: These algorithms in math are executed sequentially, i.e. in an unchanging linear order
- Recursive algorithms: These algorithms in math can call themselves and solve problems by breaking them into smaller problems and creasing a ‘base case’ to solve them all
- Divide and conquer algorithms: A type of recursive algorithm that focuses solely on breaking problems into smaller problems and solving them individually
- Dynamic programming algorithms: Known as “recursion with memory”, these algorithms in math break down problems into smaller problems and store the solutions
- Greedy algorithms: These algorithms in math make decisions on what to do based on the stage they’re in, not the overall problem
- Brute force algorithms: These algorithms in math try every possible solution until they find the right one, which can be effective, but also highly time-consuming
- Backtracking algorithms: These algorithms in math build solutions as they go, and abandon a path if they can’t find a solution to it
We can also categorise algorithms by their purpose:
- Sorting: Algorithms that are based on sorting data or items into a specific order
- Searching: Algorithms designed to find a certain entity within a database
- Graph algorithms: Algorithms dedicated to using graphs, like finding the shortest path to a destination
Difference between different types of algorithms
The difference between types of algorithms primarily lies in their structure and their purpose. Sorting algorithms and graphing algorithms have different goals, and therefore will be carried out in different ways.
Some algorithms, like sequential algorithms, will go through each step in order, while others will go through steps in an inconsecutive order, like backtracking algorithms. Some algorithms will aim to solve a problem with one overarching solution, while others (like the different types of recursive algorithms) will use multiple methods and solutions to reach their resolution.
Equations and formulations in algorithm math
There are some crossovers with formulas and algorithms. Both are set instructions designed to solve a problem, but algorithms usually offer more steps and more methods of solving the problem.
Let’s look at algorithm math examples. Length x width is a common formula to solve the area of simple shapes like rectangles, while algorithms are generally more complex and involve more steps. An algorithm, however, won’t always be structured like an equation or expression and will often include multiple steps.
Some formulas can be presented as algorithms — for example, the quadratic formula can be split into its individual parts and written as an algorithm. Equations, meanwhile, often form one step of an algorithm
Writing expressions for math algorithms
Writing expressions for math algorithms isn’t all that different from writing expressions more generally. Often, algorithms will contain expressions or equations as one of their steps, or their steps may break down each stage of an expression or equation.
If you’re breaking down an expression for an algorithm, you may need to break it down into its individual steps and provide clear guidance on what to do in each step. To explore algorithm examples math, if you have the expression (4 + 3) x 6, you could write it as the following algorithm:
- Combine 4 and 3 together
- Multiply the result (7) by 6
- Write down your answer (42)
Algorithm examples
There are lots of mathematical algorithms examples around us, from predefined algorithms used in scientific and math calculations to algorithms we can find in the technology we use in our daily lives.
Math algorithm examples
- Making a cup of tea in a step-by-step process
- A recipe for a meal, such as a spaghetti bolognese
- The Euclidean algorithm, which helps us find the greatest common divisor of two numbers
- The Sieve of Eratosthenes is an ancient algorithm designed to find all prime numbers up to a given limit
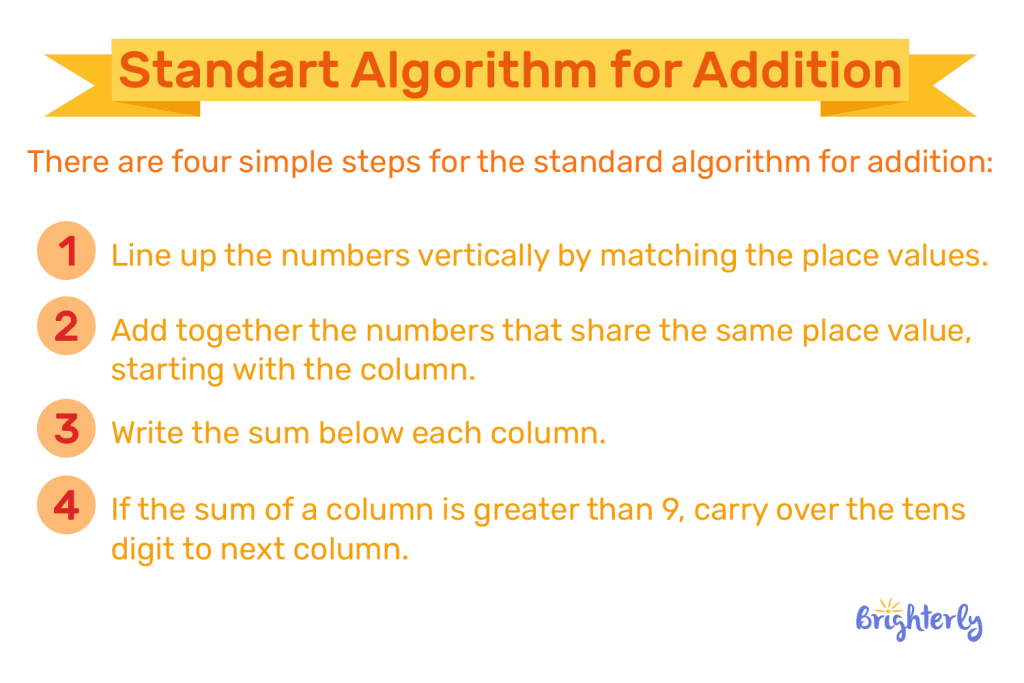
- Long division, which uses multiple steps to solve a division problem
- Dijkstra’s algorithm is an algorithm designed to find the shortest path from one given coordinate to another, and is used in GPS systems
Mathematical algorithms: Practice problems
Now, it’s time to try your hand at some problems around algorithms. By trying out these practice tests, you’re familiarizing yourself with how to solve algorithm math problems, which sets you up for success in your class and future exams.
- Write a sequential algorithm that guides someone to make a cup of coffee the way you like it
- Give some examples of divide and conquer algorithms in math
- Develop an algorithm to solve a quadratic equation
Conclusion
Here, we’ve answered the question, “What is an algorithm in math?” and given you an algorithm calculation example. We’ve also explored their properties and how to write expressions in algorithms.
Now you know everything there is to know about algorithms, you can start to break down the steps in algorithms and create your own! You’ll also start to notice the algorithms all around you in daily life, from getting to school each morning to brushing your teeth!
Mathematical algorithms: Frequently asked questions
What is an algorithm in mathematics?
In mathematics, an algorithm is a step-by-step process that guides you through solving a problem and achieving a solution. Mathematical algorithm examples include binary searches, operations like addition and subtraction and formulas like the quadratic formula.
What are the properties of algorithms?
Algorithms have many properties, including definiteness (each step is clearly defined), finiteness (they must have a finite number of steps), feasibility (they must be doable) and input and output (what is required and what will be achieved must be clearly defined).
What are the types of algorithms in mathematics?
There are many different types of algorithms in math. These include algorithms based on their structure — sequential algorithms, recursive algorithms, greedy algorithms, dynamic programming algorithms and backtracking — plus those categorised by purpose — graphing, sorting and searching.
What is an example of an algorithm?
An example of an algorithm is the technology behind GPS systems. These systems use your coordinates, plus the coordinates of your intended destination, to map out journeys that get you from point A to B, taking in factors like speed, distance and obstacles like closed roads.






