Division – Definition, Properties, and Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on February 25, 2026
The division is one of the basic math actions that allows students to equally divide anything, from slices of pizza for a company to determining the average number of stars in the nearest galaxies.
Use this article to define division, determine division meaning in math, and learn how to explain it to your child.
What is division?
Division is a mathematical operation that involves splitting a quantity into multiple equal parts. It is often represented by the symbol ÷. Math division is a counterpoint to multiplication.
Definition of division
Division definition is simple since it’s a mathematical operation that involves the sharing of an amount into equal-sized groups. This is a versatile action that you can apply to any number except 0.
The main division rule states that you cannot divide by 0, as this operation is undefined. Keep that in mind while solving problems.
How does division work?
As we said, division works by breaking a quantity into multiple equal parts. If you want to divide 12 by 4, the result will be 3. There is no “Johny gets 4 slices of pizza, Michael receives only 2, while Miranda gets 6 slices”, as this operation is not true division. True division in math splits everything equally.
Division: Mathematical notation
There are multiple ways in which math division can be represented mathematically:
- The division symbol (÷) is the most common way.
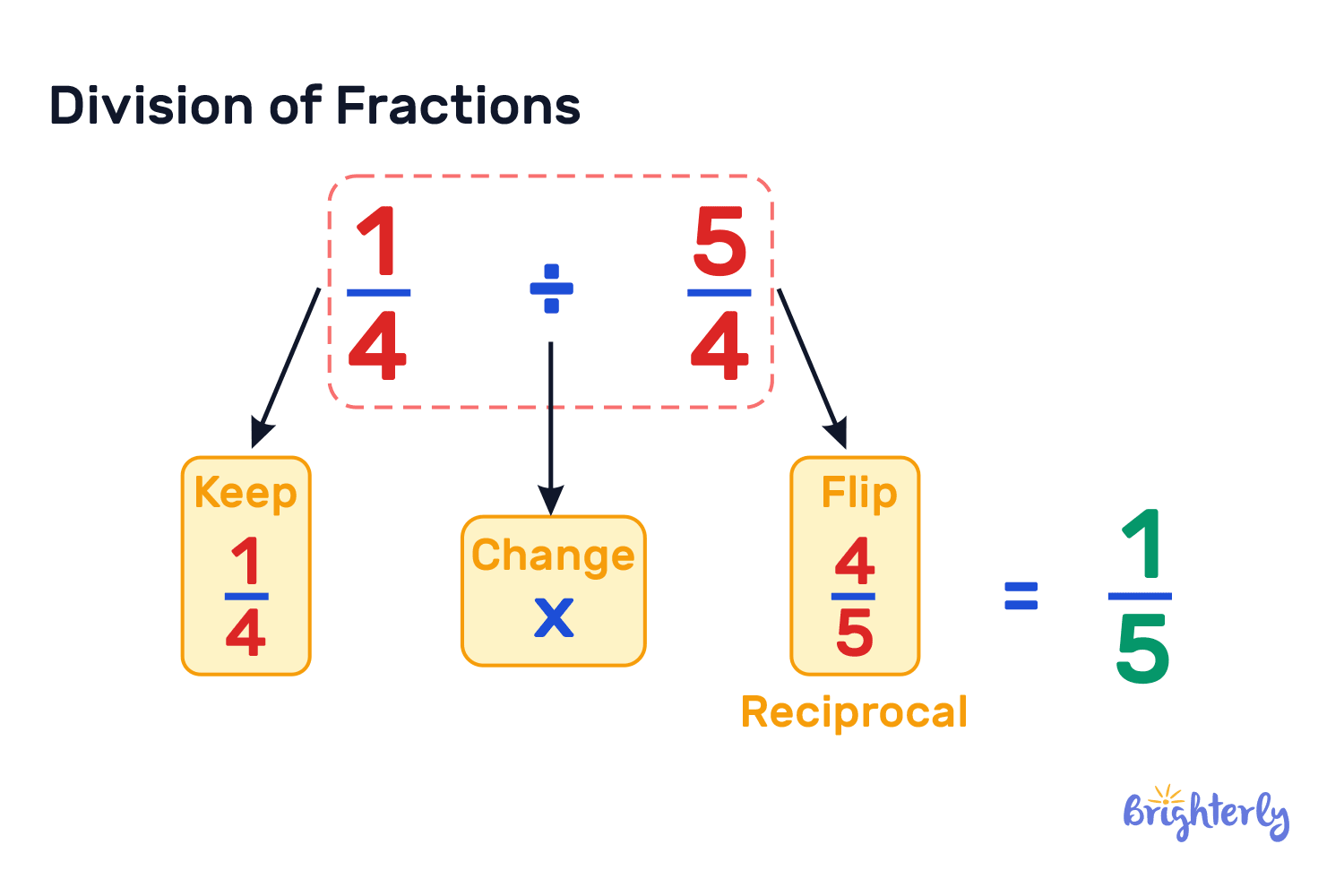
- Fraction notation, where the dividend is the numerator, and the divisor is the denominator.
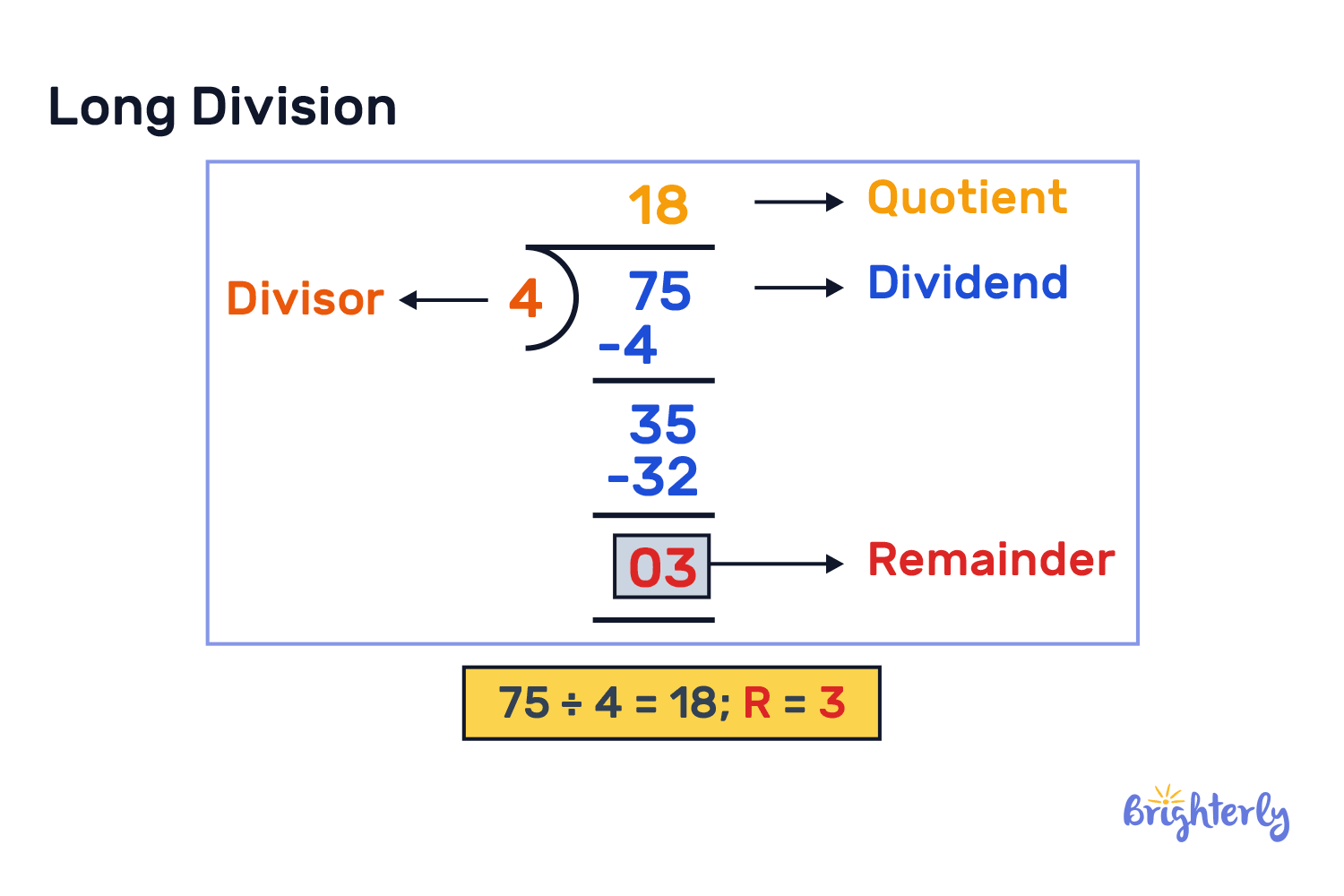
- The long division method is used to divide large numbers with a series of steps to find the quotient.
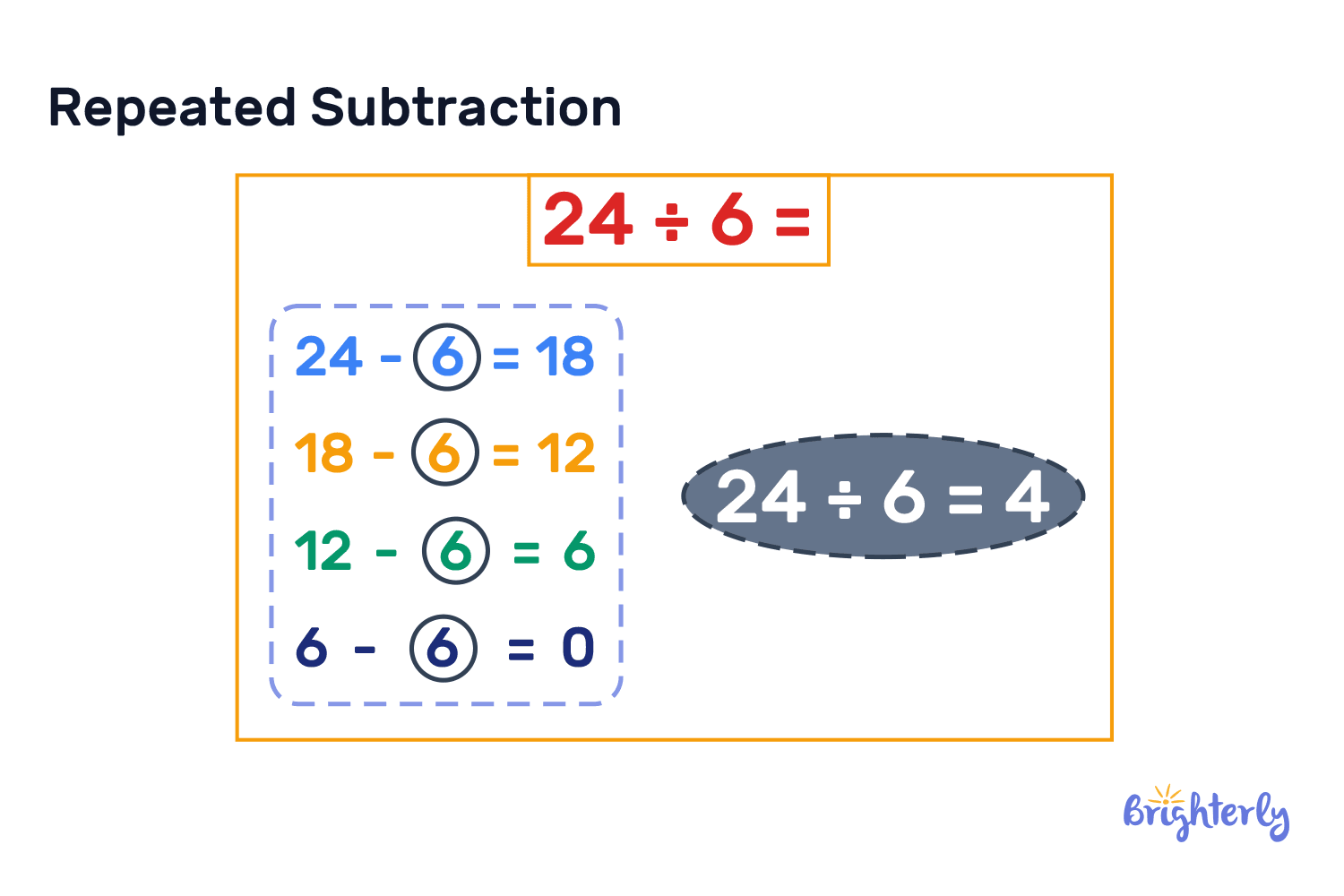
- Repeated subtraction, where division can be shown as repeated subtraction. You repeatedly subtract the divisor from the dividend until you reach 0. For example, to divide 12 by 3, you can subtract 3 from 12 four times: 12 – 3 – 3 – 3 – 3 = 0.
Division real life examples
Division examples in real life are everywhere. We’ve shared the most common ones so it is easier for your child to understand the parts of the division equation and the logic behind it.
- Sharing a pizza among a company. Imagine that you need to share 8 slices between 4 friends. You may represent it as 8 ÷ 4 =2.
- Determine the average. If a student scores 80, 90, and 100 on three tests, you can find the average by adding the scores and dividing by the number of tests: (80 + 90 + 100) ÷ 3 = 90. This means the student’s average score is 90.
Names for numbers in division equation
In the division equation, each part has its role, and it also has a name we use to refer to it. Those names are:
- Dividend: This is the number being divided.
- Divisor: This is the number that divides the dividend.
- Quotient: This is the result of the division.
Division formula
The division formula has 3 main components: dividend, divisor, and quotient. The whole process can be represented as:
Dividend ÷ Divisor = Quotient
If you have 12 cookies and want to share them equally among 3 friends, you would divide 12 by 3. In this division equation, 12 is the dividend, 3 is the divisor, and 4 is the quotient.
Properties of division
- Identity property of division
- Zero property of division
- Commutative property of division
- Associative property of division
Identity property of division
The first one of the 4 properties of division is the identity property of division. This property claims that if you divide any number (except 0) by 1, the result is the original number. It’s one of those division rules that is easy to understand, since, for example, if you have 10 apples and only one person in line, that person gets all 10 apples.
Zero property of division
The zero property of division claims that if you divide 0 by any number (except 0), the result is 0. If there are 10 apples and no person in the line, there is no one to get them, so the result is 0.
Dividing a number by 0 is undefined. This division example has no meaning; if there are 0 apples and 0 people in line, there is no purpose for calculating it.
Commutative property of division
The division is not commutative, so the order of numbers really matters. If you want to divide 10 apples between 2 people, they will each get 5 apples. But if you decide to divide 2 apples between 10 people, each of them gets only 0,2 (20%) of the apple.
This division property shows that the placement of division equation parts is crucial since 10 ÷ 2 ≠ 2 ÷ 10
Associative property of division
Last one in the list of division properties is the associative property of division, which claims that this action is not associative. that the grouping of numbers in a division problem matters. For example, (12 ÷ 4) ÷ 2 ≠ 12 ÷ (4 ÷ 2). In the first case, you’ll get 1,5, while in the second situation, the result is 6.
Solved tasks on division
Solved math problem 1
A school principal wants to share 48 new computers equally among 6 different classrooms. How many computers will each classroom receive?
Answer:
Let’s look at the division equation in parts. The total number of computers (48) is the dividend. The number of classrooms we are dividing them into (6) is the divisor. The resulting number of computers per room is the quotient. The formula is dividend/divisor = quotient, which in our case is 48/6=8.
| Therefore, each classroom will receive 8 computers. |
Solved math problem 2
An orchard harvested 120 apples and needs to pack them into boxes. If each box can hold exactly 10 apples, how many boxes are needed to pack all the fruit?
Answer:
In this problem, we divide 120 apples into 10 smaller groups. So, 120 (the dividend) is divided by 10 (the divisor), like so: 120/10=12.
| The orchard needs 12 boxes to pack all the fruit. |
Solved math problem 3
A local library has 150 new books and 5 empty shelves. If they want to put an equal number of books on each shelf, how many books will go on one shelf?
Answer:
By using the same dividend/divisor = quotient formula, we divide 150/5 = 30.
| 30 books will go on each shelf. |
Division: Practice math problems
Division worksheets
Now that you know what is the definition of division and what are the key division steps, it’s time to practice with division worksheets. They don’t look like traditional school math problems, but rather like games. They are free to download, so you can print them to ensure that your child understands crucial division steps and other aspects of this math action.
- Division facts worksheets
- Multiplication and division worksheets grade 3
- Multiplication and division fact families worksheets
- 6th grade division worksheets
Frequently asked questions on division
What defines a division?
Division is a mathematical operation that we define by splitting. More specifically, it’s the process of splitting the total amount into equal parts. It’s inverse multiplication (multiplying the number by its reciprocal) and helps us see how many of one number is contained in another number.
What are the four types of division?
The 4 types (or 4 properties) of division are the identity property of division, the zero property of division, the commutative property of division, and the associative property of division. These are the key attributes of division, its rules if you will, which guide how the arithmetic processes take place when dividing numbers.
How to explain basic division?
Explaining division doesn’t have to be complicated. An effective method you can keep in mind is the idea of fair sharing, as you are splitting a number into x equal parts. You can use physical objects, like candies, and ask your child to divide them equally among friends.