Irregular Polygons – Definition, Types, Formula
reviewed by Jessica Kaminski
Updated on October 28, 2025
Welcome to Brighterly, where we make all types of mathematical concepts, from geometry to algebra and everything in between, fun to learn and easy to understand.
Today, you’ll dive into geometry to focus on irregular polygons. These polygons stand out from regular polygons because not all of their sides are of the same length – they really break the mould.
Here, we’re going to define irregular polygon and explain its different types, along with their formulas and properties. We’ll also share some practice math questions for you so that you can test yourself on your understanding of irregular polygons after you’ve learnt all about them.
What are irregular polygons?
Irregular polygons are a type of polygon where the length of each side is different. This makes them a subcategory of polygons, which are defined as 2D closed shapes with a minimum of 3 straight sides. This means that shapes including triangles, rectangles, squares, hexagons, and more fit into the definition of a polygon.
Irregular polygons are set apart from more traditional polygons because of their lack of uniformity. Their sides of differing lengths can also create different angles, making them a particularly interesting shape in geometry.
Here are some other irregular shapes examples:
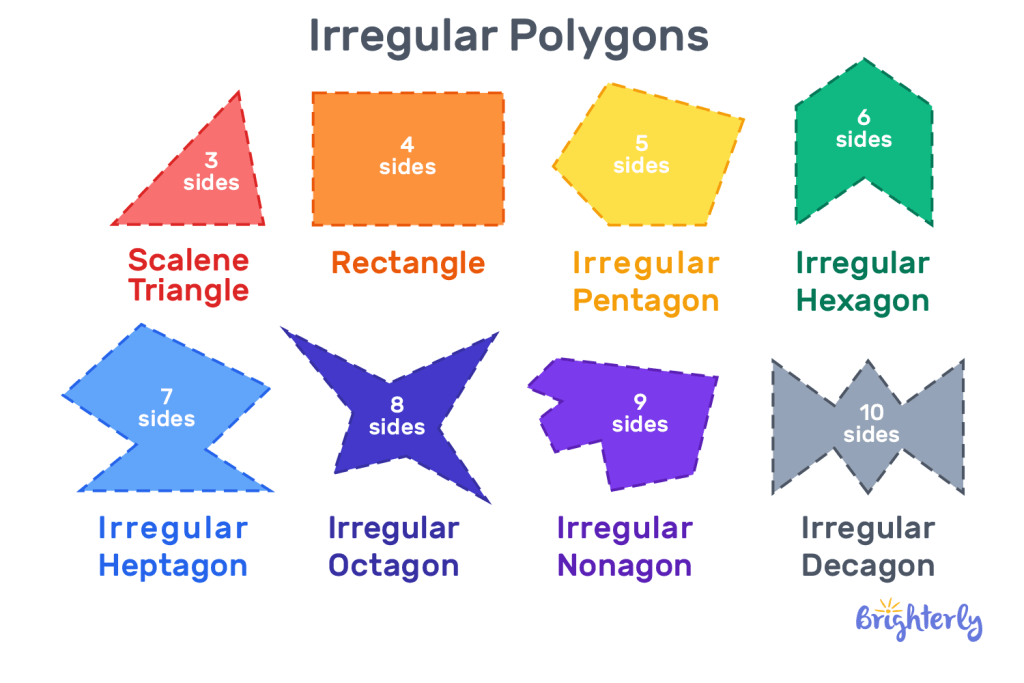
Definition of irregular polygons
The irregular polygon definition (aka non regular polygon) in its most basic form is a polygon with unequal sides and angles. It means that these shapes do not conform to the general rules around polygons.
What defines an irregular polygon is that not all lengths of its sides are the same. That’s exactly why a rectangle can also be named an irregular polygon. Learning to identify the irregularity in the line of each side can help you quickly distinguish irregular polygons from regular ones.
The irregular polygon shape can be different from regular polygons, as you can see above, because they don’t conform to the rules of standard polygons.
Types of irregular polygons
There are many different types of irregular polygons you’ll come across. Here are some of the different categories with their irregular polygon names:
- Irregular quadrilaterals: This type of irregular polygon has four sides and four angles, just like a standard quadrilateral. The scalene quadrilateral is an irregular polygon, because all of its sides are of different lengths
- Irregular pentagon: The irregular pentagon is a shape with 5 sides and angles that will not all measure the same. This irregular 5 sided shape may not look like a traditional pentagon, because its five sides can form different shapes.
- Irregular hexagon: This type of irregular polygon differs from a standard hexagon because its six sides and angles won’t be the same size
Formula of irregular polygons
With standard polygons, you have defined formulas that help you work out their area and diameter. However, with irregular polygons, there is no standardized irregular polygon formula.
So, how do you work out their area or diameter? One of the most common ways of doing this is by splitting the polygon into more common shapes that have defined formulas. For example, an irregular pentagon could be split into a triangle (aka a 3 sided polygon) and a square, making working out these dimensions much easier, even without having an area of an irregular pentagon formula.
Properties of irregular polygons
While irregular polygons can be considered rule-breakers, they also have a number of properties that make them distinguishable from regular polygons, but still uniform in their own way.
Some of these properties are as follows:
- Irregular polygons can have lengths of any size – there is no restriction – and they can have some sides of the same length, or every side can be a different length
- While all angles can be different or the same in irregular polygons, the sum of all internal angles will always add up to the formula of (n-2) × 180°, which is also the formula used to calculate the internal angles of all polygons
- You can calculate the number of diagonals in an irregular polygon using the formula n(n-3) ÷ 2
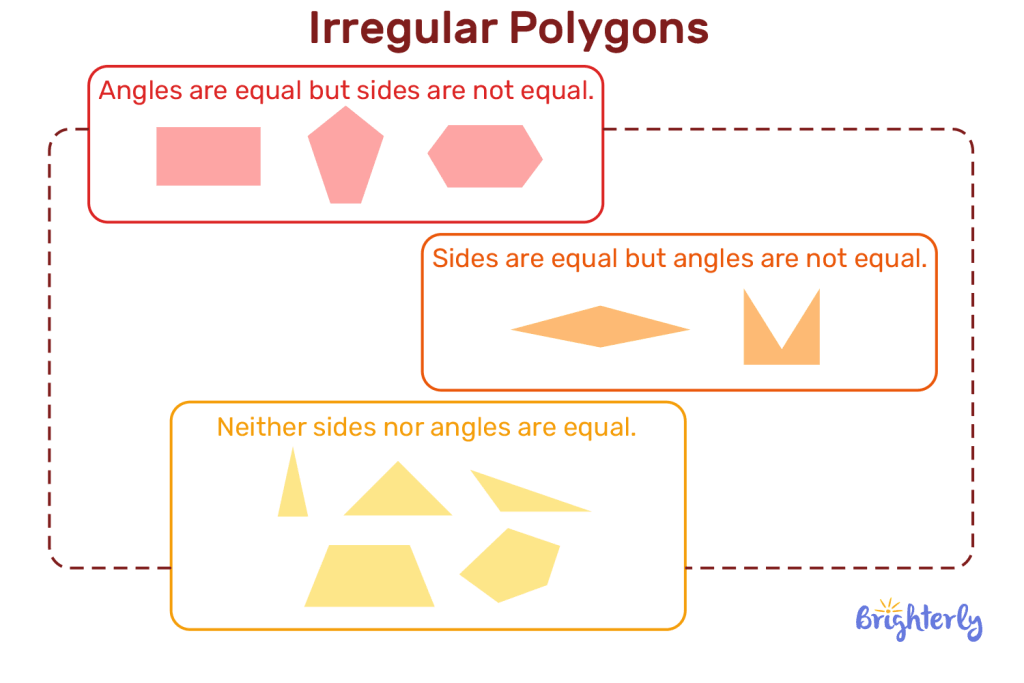
Differences between types of irregular polygons
All types of irregular polygons will adhere to the above set of properties, but they are also unique in their own right. The differences between most types of irregular polygons lie in their distinctive shapes, number of sides, areas, and diameters.
For example, when you think of a pentagon, you imagine a shape with a base and two sides on each side forming to point outwards, culminating in a point at the top. But an irregular pentagon shape can form a shape that looks more like a crown with only 2 points. That’s the beauty of irregular polygons – they extend far beyond what we consider traditional shapes.
Equations for calculating properties of irregular polygons
There are equations for calculating some of the properties of irregular polygons. Thus, you can calculate the following properties with these equations (in each formula, n stands for the number of sides):
- The sum of interior angles: You can calculate this property by using the equation (n-2) × 180°
- The number of diagonals: This property can be calculated by using the equation n(n-3) ÷ 2
However, there are some properties that you cannot calculate simply with a formula. These include the area and the perimeter of an irregular polygon. To calculate these, you can split your polygon into regular shapes, use the formulas for those shapes, and then combine your results.
Let’s use the example of an irregular pentagon that can be split into a square and a triangle. First, you’d work out the area of the square using the formula n², where n is the length of the sides. Then, you can work out the area of your triangle using the formula (base × height) ÷ 2. Then, you simply add the two numbers together.
Writing equations for irregular polygons
Writing equations for irregular polygons is easy when you have the defined formulas. Let’s take the example of working out the internal angles of an irregular 6 sided shape (hexagon). Our equation would be (6-2) x 180°, which is 720.
Equally, it’s easy to write the equation for the number of diagonals in your shape. If we again use the example of an irregular hexagon, our equation would be 6(6-3) ÷ 2 = 9.
There’s no set way to write an equation to work out the area or diameter for an irregular polygon; however, you can combine equations when you split it into different shapes. If we use our above example of a pentagon that can be split into a square and a triangle with assigned side lengths, our equation can become (52) + [(4 x 3) ÷ 2] = 31.
Practice problems on irregular polygons
Now, it’s your turn! Try out the problems below to see how well you’ve taken in this information on irregular polygons. Write down your answers, and use a sheet of paper to draw shapes or show your workings if you need to.
- You have an irregular quadrilateral with side lengths of 3cm, 5cm, 7cm, and 9cm. What is the perimeter of this irregular quadrilateral?
- You have an irregular pentagon with the interior angles of 100°, 120°, 110°, 130°, and 80°. Do these angles follow the formula that determines the sum of interior angles in irregular polygons?
Conclusion
Here, we’ve taken you through the definition of an irregular polygon, the properties of these shapes, and the equations associated with them. We also shared some irregular polygon examples so you can see for yourself how different irregular polygons can be. Now, you should be confident in identifying and working with them in math class!
Although it might seem complex to work out dimensions like the area and diameter of an irregular polygon, now that you know what to do, you’ll easily be able to solve these types of problems too! Now go forth and confidently apply this knowledge to your geometry learning and become a master of math.
Frequently asked questions on irregular polygons
What are irregular shapes?
Irregular shapes are shapes that don’t follow the standard rules of shapes in those categories. In irregular polygons, for example, sides aren’t uniform in length. Beneath this, we have subsets like irregular quadrilaterals, irregular pentagons, and irregular hexagons.
What is an irregular polygon?
An irregular polygon is a 2D shape with 3 or more sides that are not all the same length. These polygons differ from standard polygons because their sides are of different lengths. They can have some sides that are the same length and some that aren’t, or all sides can be different lengths.
How to find the area of irregular polygons?
There is no standardized formula for finding the area of irregular polygon because they can vary dramatically in shape and size. To calculate the area, you can divide your shape into two regular shapes, such as splitting an irregular pentagon into a triangle and a square.
What is the difference between regular and irregular polygons?
The difference between regular and irregular polygons is that in regular polygons, all sides have the same length, whereas in irregular polygons, they don’t. Because the sides are of varying lengths, the angles are also of different sizes in irregular polygons, while they are uniform in regular polygons.






