Length Width Height – Definition with Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on January 7, 2026
Welcome to Brighterly, your trusted partner in learning everything there is to know about math! Today we’re going to explore the three dimensions that define our 3D world: length, width and height. Here, we’ll share examples of these dimensions, length width height order and how to measure them. We’ll also share practice math problems and cool worksheets so you can further your learning!
What is length and width?
Length and width are dimensions that apply to 2D and 3D shapes and objects. The length is the longest side, measuring end to end, while the width is the shorter dimension from side to side. Width is sometimes known as breadth.
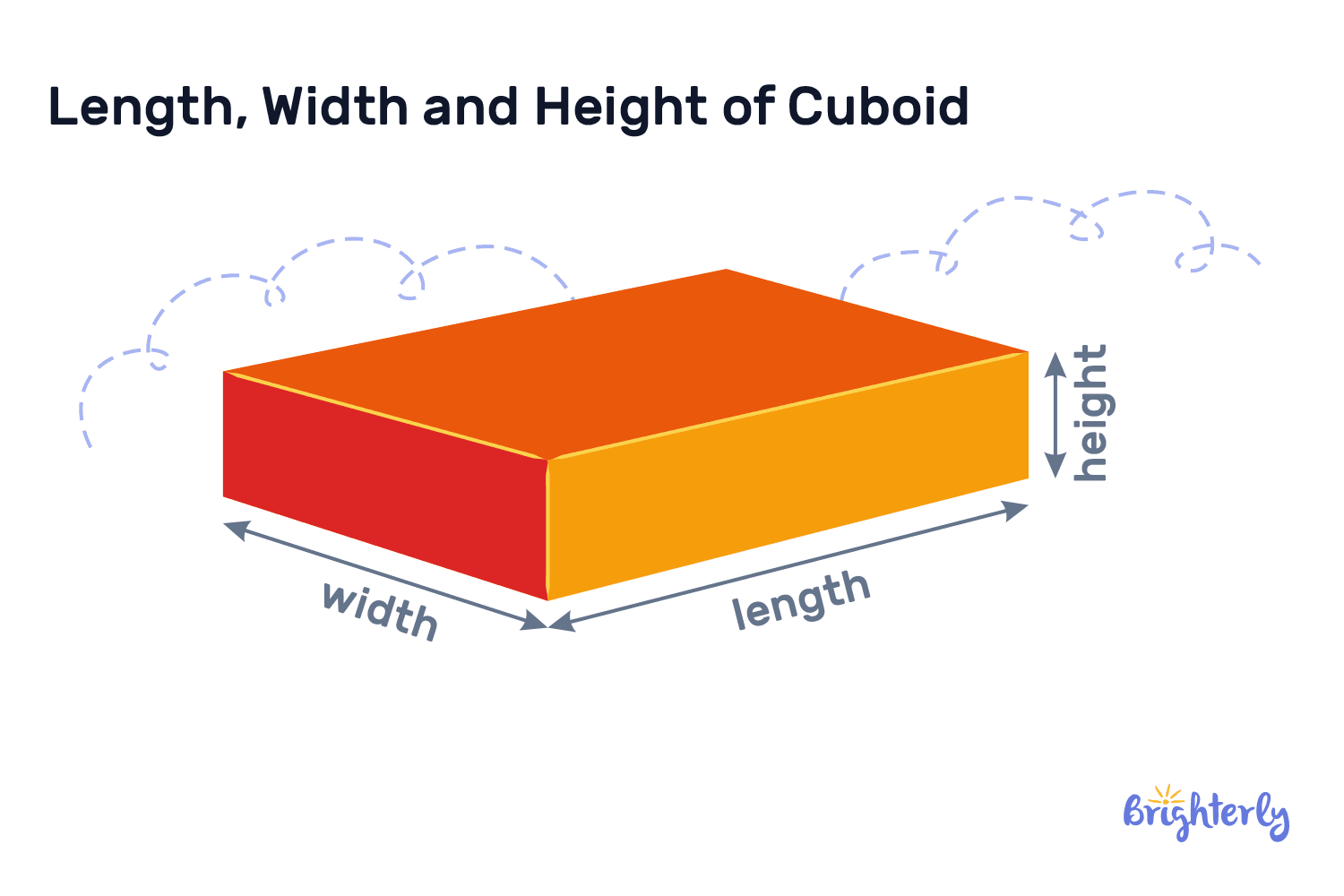
Is length the same as depth?
The measurement of something from end to end is referred to as “length.” “Depth” indicates how deep something is by measuring the distance from the top down or front back. Different dimensions are measured by length and depth. In particular, length is a linear measurement that captures an object’s longest extent from end to end. It is commonly used when talking about the separation between an object’s tips. Depth, on the other hand, evaluates an object’s depth or profundity by measuring how far it extends from the top surface or from front to back.
In order to understand an object’s size from one end to the other, we may ask about its length. Generally speaking, length is a simple measurement that is frequently, though not always, considered in a horizontal context. On the other hand, depth can be seen as more vertically oriented and gives information about how far something extends below a surface. This can be metaphorical, like knowledge, or physical, like water.
Let’s explore further, what is length and width?
What is the difference between length and width?
While width describes the measurement of something from side to side, usually perpendicular to the length, length refers to the measurement of something from end to end. The difference between length and width, in its most common sense, length describes an object’s maximum length from one end to the other. In contrast, width is commonly defined as the measurement of an object from side to side, usually at a right angle to its length. As a result, in a rectangular object, width typically denotes the shorter dimension and length the longer.
What are length, width and height?
Length vs width vs height are the 3 dimensions that apply to 3D objects. Length is the longest measurement, and width measures the object side-to-side. We then add a final dimension of height, measuring vertically from the base to the top.
This additional measurement moves a shape from 2 dimensions to 3 dimensions. If you’re wondering, “Does width come before height?”, generally, the answer is yes!
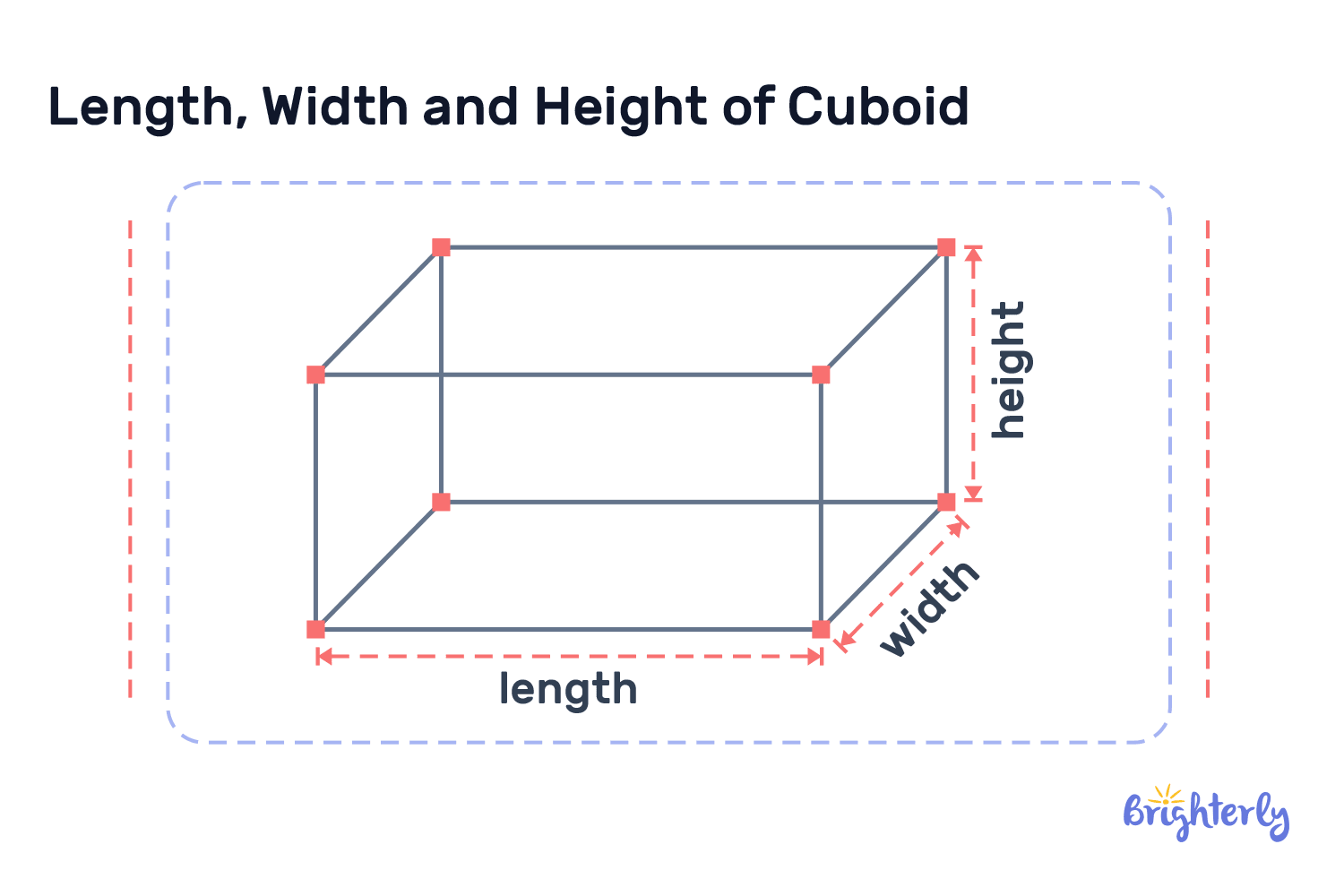
How to measure length width height?
You can measure length, width, and height using various measuring tools, including tape measures, rulers, or even laser distance measurers. The tool will depend on the size of your object and should be appropriate to it. For example, if you have a small box, you can measure its height width length with a ruler. Larger items may require tape measures or laser distance measures.
First, identify the length and measure that accurately from end to end, placing the 0 marker on your measuring tool at one end of the length, then marking where it finishes. Next, repeat these steps to measure your width, which is perpendicular to the length. Then, measure your final dimension, the height, from base to top.
Length, width height formula
When we use the height length width formula (length x width x height), we get the volume of an object.
Volume = L × W × H
To find the area of the base of a cuboid, multiply the length times width. Then multiply by the height to get the volume. The volume represents how much space the object occupies and the space available inside. In real life, we use this to find out how much a container can hold or how much space an item takes up. As a l x w x h example, a box with a length of 2 meters, a width of 1 meter, and a height of 1 meter has a volume of 2 cubic meters.
We can also measure the Surface Area, knowing the length, width, and height.
Surface Area = 2 × (L × W + L × H + W × H)
This calculates the total area of all sides of the object.
Length width height example
There are examples of objects with defined length, width, and height all around us, including:
- An A4 sheet of paper, which has a length of 297 mm, a width of 210 mm, and a height of less than a mm
- A brick, with a standard length of 200 mm, a width of 100 mm, and a height of 76 mm
Sometimes length, width, and height are expressed as length, width depth, but this is incorrect, as width is the same as depth.
Length vs width
The distinction between a figure’s width vs length is that the former denotes its longer side, while the latter denotes its shorter side.
The width indicates how broad or wide the figure is, and the length indicates how long it is. Another name for the width is breadth. For instance, we can quickly determine that a rectangle’s length is 8 cm and its width is 3 cm if its two sides are given as 8 cm and 3 cm, respectively. To understand the distinction between a shape’s length and width, look at the rectangle below.
Length is commonly used to describe an object’s measurement from start to finish. In contrast, width is used to calculate an object’s width from side to side. In many disciplines, including mathematics, engineering, and various types of design, the use of both length vs width becomes especially clear and important, helping to precisely define and create objects or spaces.
Length x width x height
The length, width, and height of a geometrical figure, such as a rectangular prism, also called a cuboid, are used together to determine its volume. Multiplying the LWH of a cuboid gives us its volume. This means that Length x Width x Height = Volume of Cuboid. Hence, the capacity or volume of any rectangular box or cuboid can be determined by multiplying their three dimensions. Here is an example to help you understand.

Example: Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 10 cm, width is 6 cm, and height is 5 cm.
Solution: The formula below can be used to calculate the volume of a cuboid:
Volume of Cuboid = Length x Width x Height
In this case, we get Volume of Cuboid = 10 x 6 x 5 = 300 cm³.
Length width height of a box
It’s easy to work out and measure the length width and height of a box. The longest side of the box, running from one end to the other, is the length. Then, your width is the measurement perpendicular to the length across the box. Finally, the vertical measurement from top to bottom is your height.
Units of measurement for length, width, and height
We can use many units of measurement to measure length height width. In the US, we use the imperial system, so we’ll often measure length, width, and height in inches, feet, yards, and miles, depending on the size of our object. Elsewhere, the metric system of millimeters, centimeters, and kilometers is used.
Importance of accuracy in measurement
It’s important to measure our width and length, and height accurately, especially in real-world contexts like manufacturing, construction, science experiments, and even cooking. By measuring these dimensions precisely, we can ensure pieces fit together correctly, the right quantity of materials is used, or we’re using the right containers. Inaccurate measurements in real life can cause many problems!
Length width height order
In order to describe an object’s dimensions clearly, length and width and height are usually listed in the following order:
- Length (L) – the longest side of the object, measured from end to end.
- Width (W) – the side perpendicular to the length, often the shorter horizontal dimension.
- Height (H) – the vertical measurement, from the base to the top.
Example: A box labeled 10 × 5 × 8 means:
- Length = 10 cm
- Width = 5 cm
- Height = 8 cm
Following this order ensures that dimensions are consistently communicated, especially in construction and geometry.
Solved examples on length width height
Example 1: Find the volume of a box with length 4 cm, width 3 cm, and height 5 cm.
Solution:
Volume = Width x Length × Height
Volume = 4 × 3 × 5 = 60 cm³
| So, the volume of the box is 60 cm³. |
Example 2: A box has a volume of 120 cm³. Its length is 10 cm, and width is 4 cm. Find the height.
Solution:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
120 = 10 × 4 × Height
120 = 40 × Height → Height = 120 ÷ 40 = 3 cm
| So, the height is 3 cm. |
Example 3: Find the missing length if the box has volume 84 cm³, width 7 cm, and height 3 cm.
Solution:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
84 = Length × 7 × 3
84 = 21 × Length → Length = 84 ÷ 21 = 4 cm
| So, the length is 4 cm. |
Example 4: True or False – A box with length 6 cm, width 2 cm, and height 5 cm has a volume of 60 cm³.
Solution:
Volume = 6 × 2 × 5 = 60 cm³
Answer:
| True |
Example 5: A box has volume 90 cm³ and height 5 cm. If the width is 3 cm, find the length.
Solution:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
90 = Length × 3 × 5
90 = 15 × Length → Length = 90 ÷ 15 = 6 cm
| So, the length is 6 cm. |
Length width height: practice math problems
Length width height worksheets
Now you know all about length, width and height, put your knowledge into practice with our cool math worksheets!
- 2D and 3D shapes worksheets
- Measuring lengths worksheets
- Measurement grade 1 worksheets
- Surface area and volume worksheets
Frequently Asked Questions on Length Width Height
Can width be longer than length?
Yes, sometimes the width can be longer than the length. Usually, length is our longest dimension, but this rule is flexible. In real life, TV screens and computer monitors have width as their longest dimension, so it depends on the specific context.
What if my object is round, like a ball?
For round objects, we don’t use width length height. Instead, we measure the radius (the distance from the middle to the surface of a sphere) and diameter (the longest distance from one end of the object to the other, that passes through the middle).
Is volume always calculated by length x width x height?
No, we only use the length times width times height formula for rectangular or cubic objects. There are different formulas for other shapes. For example, the volume of a sphere formula is 4/3π(radius3), and the volume of a cylinder formula is π(radius2) x height.







