Operations – Definition With Examples
Updated on December 1, 2025
Mathematical operation is the foundation for working with numbers in any circumstance. Here at Brighterly, we’ll look at the main properties of the basic operations and how they differ in equations to provide you with a better understanding of how these operations work as well as why they’re so important.
What are operations?
Actions taken according to a specific set of guidelines are referred to as operations. Frequently, they are used for math problems and real-world comparisons.
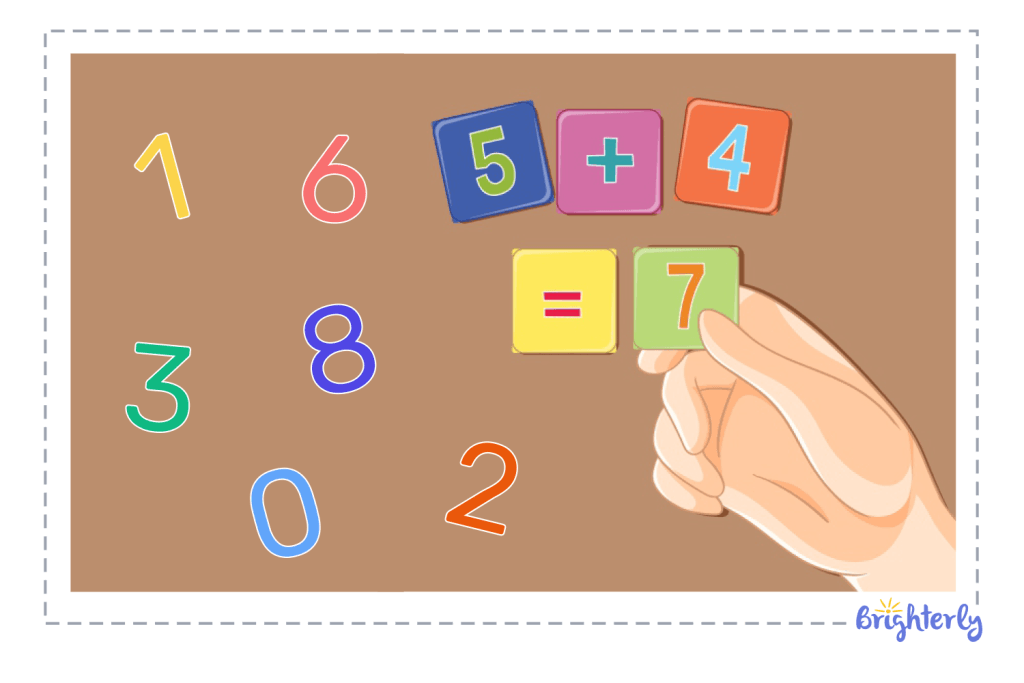
In real life, actions like dividing a chocolate bar with friends or adding up your allowance represent fundamental operations in math. Several key properties of these operations will be discussed here, as well as the real-life sense of numbers.
Operation math definition
The basic operations in mathematics include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Math also has other helpful operations like exponentiation, logarithms, and trigonometric functions. In simple terms, operations definition in math refers to the basic actions we apply to numbers to get new results.
Understanding the operation meaning in math helps us see how numbers interact and lays the groundwork for tackling more advanced concepts, which we’ll explore further in this article.
For now, you should know that all mathematical processes are built on four main operations:
- Addition (+) — Combines two numbers to make a larger value.
- Subtraction (-) — Finds the difference between two numbers.
- Multiplication (x) — Shows the total when one number is repeated several times.
- Division (÷) — Breaks a number into equal parts.
These are the core operations in math to start exploring if you’re new to the topic.
Properties of operations
Properties in math help us understand how numbers work.
- The Commutative Property states that we can change the order in multiplication and addition equations and still receive the identical result.
- According to the Identity Properties, adding 0 or multiplying by 1 leaves the number unchanged.
- Adding and multiplying are related by the Distributive Property.
- Associative Properties allow numbers to be grouped differently without affecting the outcome of the calculations.
Understanding these properties is important in the operation definition math because they show that mathematical operations always follow reliable patterns.
Properties of basic math operations
Some math rules help us add and multiply numbers more easily.
- The Associative Property means that the way we group numbers doesn’t change the answer.
- The Distributive Property explains how multiplication works with addition. For example, we can break a complex equation of 4 × (3 + 2) into 4 × 3 + 4 × 2 and get the same result while solving both.
Number and operations
To distinguish between the two concepts, think of numbers as the building blocks, and operations as how we use them. Add 5 + 3, subtract 10 – 4, multiply 2 × 6, and divide 12 ÷ 3 — these are all examples of operations. But inside them, we complete actions with numbers.
Difference between different operations
It’s important to remember that mathematical operations are unique, even if they seem similar at first glance. Multiplication often increases a number, and division often decreases it, but this depends on the values used.
For example, multiplying by a number less than 1 makes the result smaller, and dividing by a number less than 1 makes the result larger. Mathematics’s more complex operations, logarithms and exponentiation, function differently and have specific applications.
Mathematical operations examples
The most common math operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and determining powers and roots of numbers. Let’s take the equations like 2+3=5 and 10×2=20 for instance — both demonstrate the action of addition.
Basic operations examples
The four most popular operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. For instance, 4 + 7 = 11, 9 – 3 = 6, 5×3=15, and 12÷4 = 3. These serve as the basis for all other mathematical computations.
Equations involving operations
Simply put, an equation says “these two sides are equal.” Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing are typically mixed in. Use multiplication and subtraction to determine the value of x in number operations such as 3x – 2 = 4.
Writing equations involving basic operations
Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing real-world problems into basic equations is one of the best math skills. For instance, you can write 4 × 5 = y, where y is the total cost, if you purchase four notebooks for $5 each. The key to mastering math is being able to translate common problems into numbers and signs like this.
Advanced operations and their equations
You’ll discover more interesting things about math as you explore it. As an example, 32 = 9 simply means that 3×3 is 9. Thus, we can always break down a complex operation to make it more understandable and easier to solve.
Practice problems on operations
- Solve: 7 + 15 ÷ 5 – 3
- Find the missing number: 4×? – 6 = 10
- Simplify: (8 + 2)×5 ÷ 5
- Write an equation using addition and multiplication to represent: “You have 3 boxes, each containing 7 pencils, and you receive 5 more pencils.”
Conclusion
When you understand the definition of operations, you can use them to solve real-life problems and see how numbers interact. This key part of math helps put basic numbers into meaningful answers. From dividing a bill to solving complicated problems, operations bring math to life.
Frequently asked questions on operations
What is an operation in math?
The operations math definition is a way to take one or more numbers (or variables) and produce a new value. The classics are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division — your go-to tools for pretty much any math problem.
Why are operations important in math?
Operations are important in math because they allow us to complete actions with numbers, like comparing them, understanding their relationships, and solving real-world problems.
Are there more operations beyond the basic four?
The extra operations beyond the basic four are exponentiation (raising to powers), roots, logarithms, and even trig functions like sine and cosine.






