Subtraction – Definition, Symbol, Examples, Practice Problems
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on December 19, 2024
Every day, we reduce something. This can be the number of days in a month, the amount of cereals left in the box, or even the number of episodes in our favorite show.
This concept in math is called subtraction. It is the reduction of something by a certain amount.
Here, we answer questions such as “What does subtract mean?” and “How do we subtract?”.
Keep reading to learn more about the subtraction definition, examples, and subtraction facts that make the calculation easier.
What Is Subtraction?
Simply put, subtraction is the removal of a quantity from another quantity. When we remove one from another, this arithmetic operation determines what is left of two quantities, numbers, values, objects, and so on.
What is Subtraction in Math?
In math, subtraction is one of the four basic arithmetic operators (multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction).
Subtraction is used to find the difference between two numbers. For instance, for the numbers 7 and 5, the difference is 2. We represent subtraction with the sign (–). Therefore, if we were to subtract 5 from 7, it would be expressed as 7 – 5 = 2.
Definition of Subtraction
We may define subtraction as the mathematical system of removing a quantity from another to find the difference. We may also refer to subtraction as “taking away”. What we call “the difference” is what is left of the numbers after subtraction. When we subtract 3 from 8, the difference is 5.
How to explain subtraction to kids
Subtraction is explained to kids by using concepts they are already familiar with. Here are some tips to help you do so:
- Begin by giving a subtraction definition for kids. Use the phrase “taking away” so they can understand that it means to remove from something
- Engage their visual senses by displaying subtraction in action through toys and objects separating them to form parts of a subtraction problem.
- Relate real-life scenarios that require subtraction, such as calculating change or what is left after sharing snacks, etc.
- Give them word problems to improve their critical thinking skills to see for themselves how they can apply subtraction.
Subtraction examples
Some subtraction examples and situations where we use subtraction include:
- When calculating change left after purchasing goods
- We may use subtraction for gauging health and fitness such as calculating how much weight has been lost and how much more needs to be lost before reaching the goal.
Symbol of Subtraction
The symbol of subtraction is the “ – ” sign. This sign may also be referred to as the minus sign. It is placed between the numbers which are to be subtracted. The number on the right of this symbol is the number that we subtract from the number on the left of the symbol.
To illustrate, if Mae had 7 crayons and her little brother takes away 4, we would express it as:
7 – 4 = 3.
Formula of Subtraction Operation
We can break down the parts of a subtraction equation to express the formula:
- Minuend: This is the number that we subtract another number from
- Subtrahend: This is the number that subtracts from the other number (minuend)
- Difference: This is the result of the subtraction process.
Therefore, the formula of the subtraction operation is Minuend – Subtrahend = Difference.
The subtraction terms can therefore be input into our previous example of Mae and her crayons which means:
The amount of crayons Mae had (7) is the Minuend, the crayons her brother takes away (4) is the subtrahend, and the result (3) is the difference.
What Is Minus in Math?
Minus, also represented by the “ – ” sign, is an alternative way to represent subtraction in math. However, minus has other uses other than just subtraction.
Uses of Minus Sign
As we stated above, minus has the same subtraction meaning. it performs the task of reducing or deducting one quantity from another.
However, it also has other uses, including:
For negative integers:
Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero. We use the minus sign in front of a whole number to represent a negative integer such as how – 9 is the negative integer of the number 9.
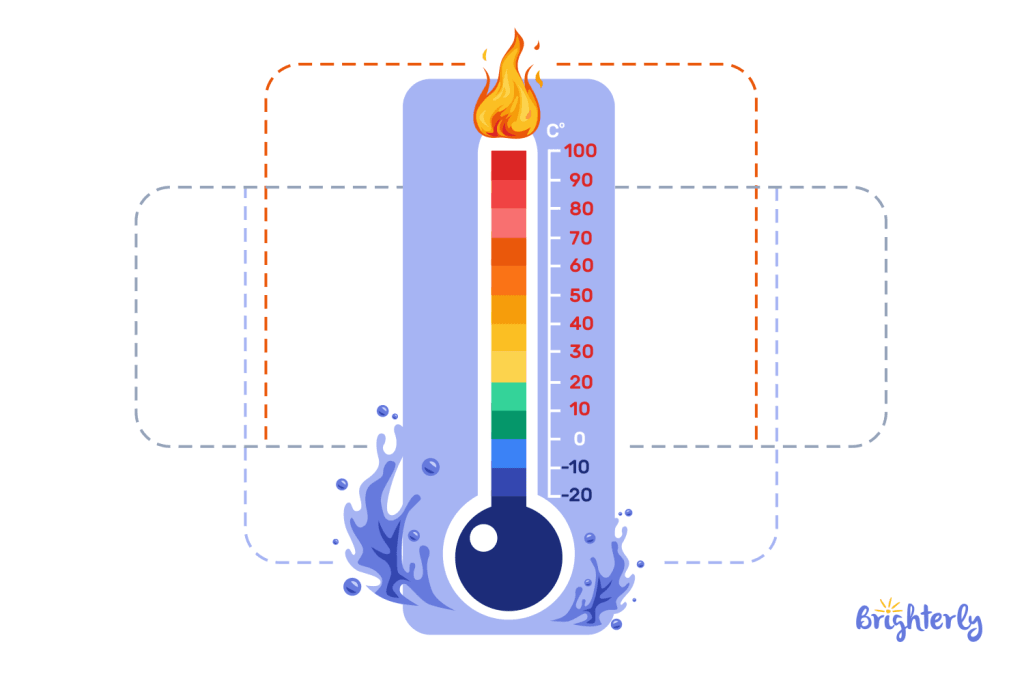
For temperatures below 0
We use the minus sign to indicate temperatures below 0° in Celsius (°C ). When the temperature falls below 0° in °C, it is below freezing point. Therefore, if the temperature is –9°, for example in °C, it is below freezing.
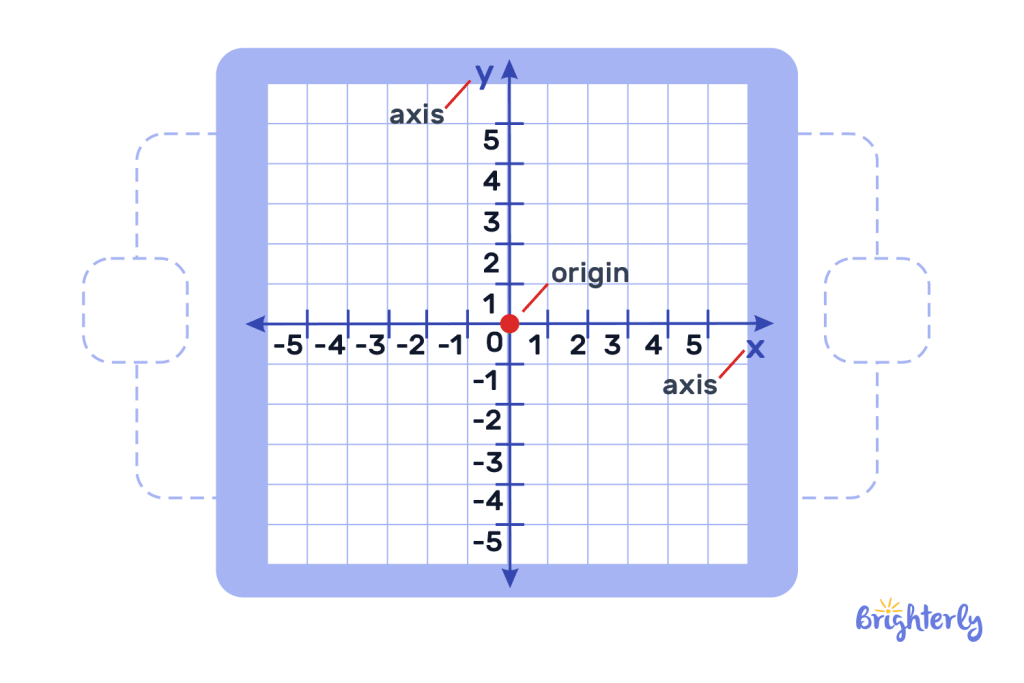
For the negative direction in graph
The minus sign also helps show the negative coordinates in a graph for the x-axis and the y-axis. For the x-axis (the horizontal axis), the negative coordinates are to the left of the origin (center of the graph), and in the y-axis (the vertical axis), the negative coordinates are below the origin.
How To Solve Subtraction Problems?
We solve subtraction problems through three basic steps:
- Identify the Minuend and the Subtrahend
- Remove the subtrahend from the minuend
- Write what is left. This is the difference.
Subtraction Without Regrouping
Subtraction without regrouping happens when the digits in the place values of the minuend are larger than or equal to the digits in the subtrahend. Therefore, we do not need to regroup or borrow because subtraction can be done directly.
For instance, in the equation; 52 – 21, we can easily subtract each digit directly, starting from the rightmost side, i.e., 2 – 1 = 1, and 5 – 2 is 3 when we subtract, meaning the answer is 31.
Subtraction With Regrouping
Here, a digit (or digits) in the subtrahend is larger than the corresponding digit(s) in the minuends even though the value of the minuends is larger. We have to regroup or “borrow” from the next place value in these cases.
For example, if we are to subtract 19 from 25 (written as 25 – 19), 9 (the one-place value of the subtrahend) is larger than 5 (the place value of the minuend). Therefore, we must regroup or “borrow” from the next place value. To do this, we subtract 1 from the next number. In this example, 2 is the next number, meaning it becomes 1, and 5 becomes 15. Now, we subtract 9 from 15, which results in 6.
Next, we subtract 1 from 1 (previously 2), which gives 0. The answer to 25 – 19, is therefore 6.
The steps to regrouping in subtraction are:
- Observe the numbers to see if the digits in the minuend is larger than the digits in the subtrahends
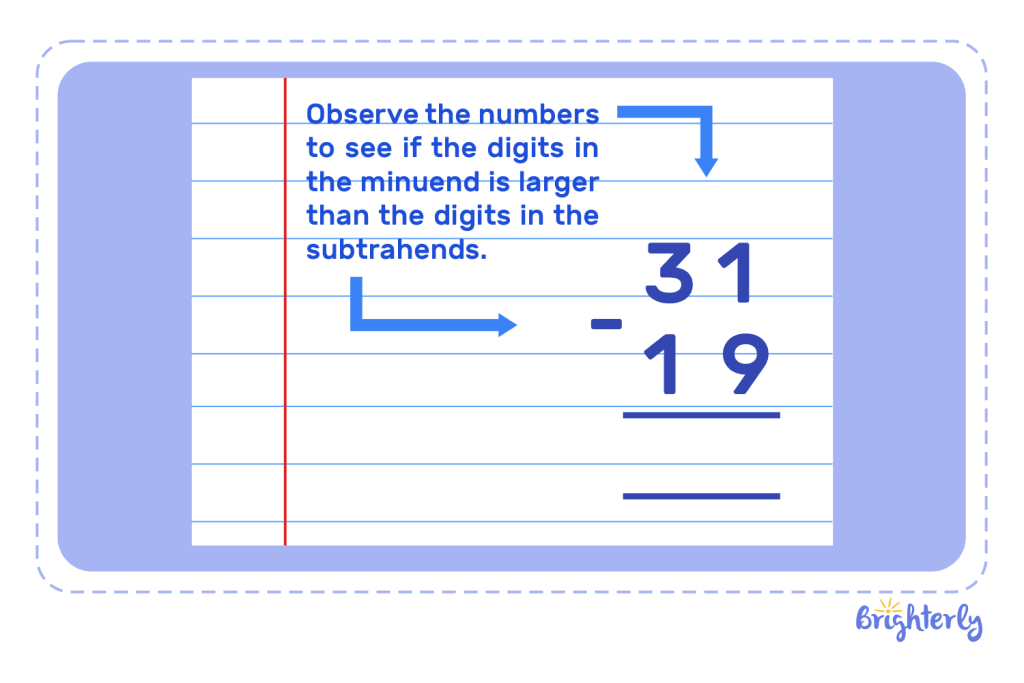
- If so, borrow 1 from the next number
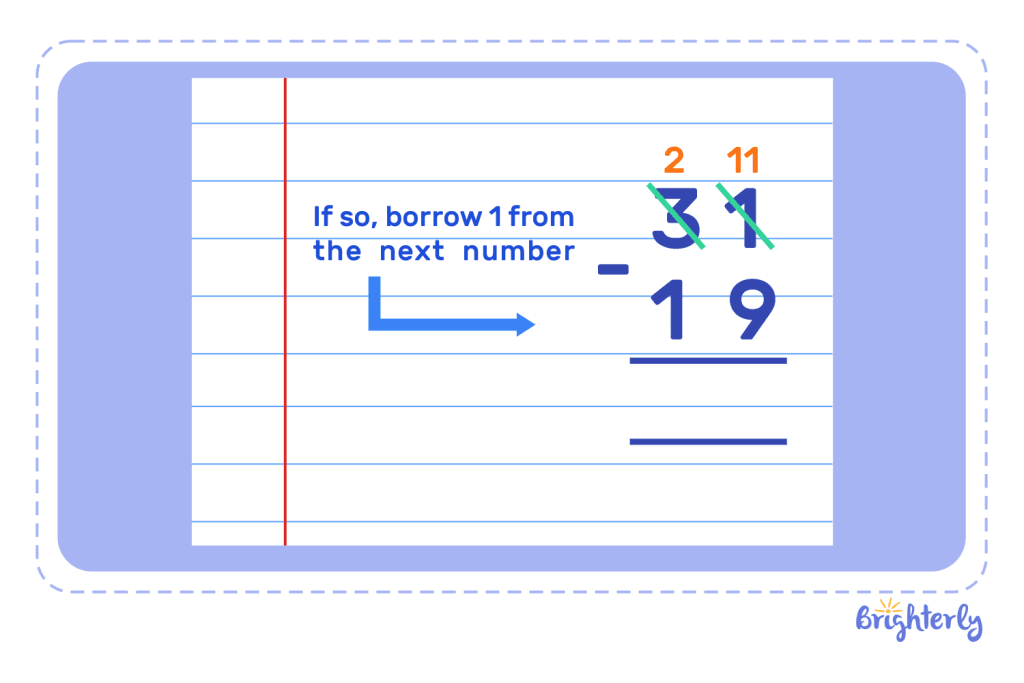
- Carry on with the calculation with the new digits
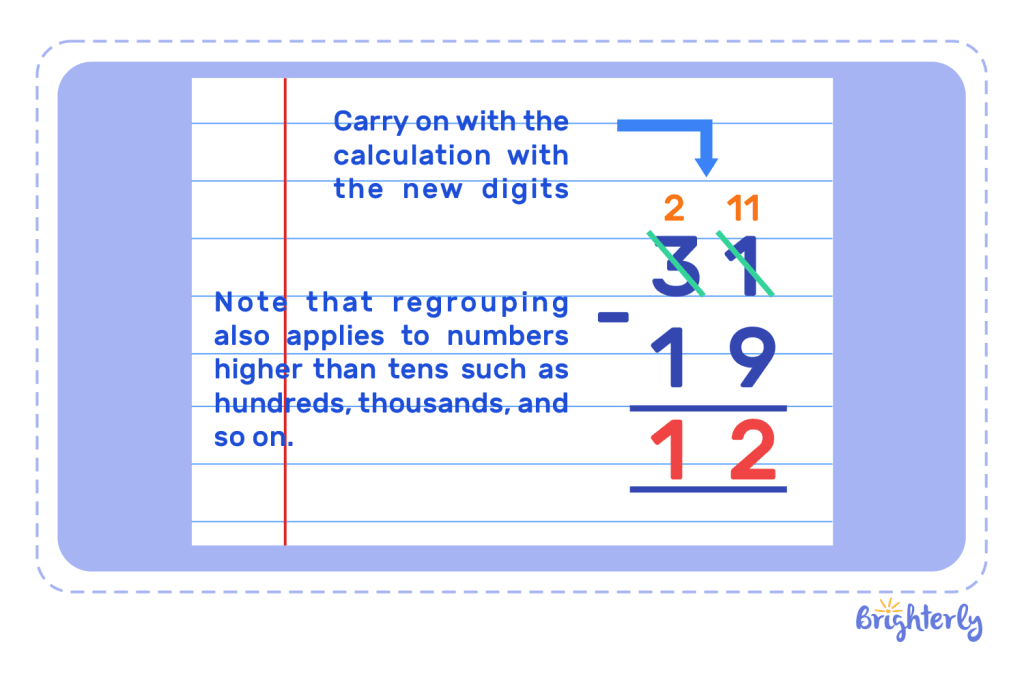
Note that regrouping also applies to numbers higher than tens such as hundreds, thousands, and so on.
Subtraction Table
A subtraction table is a chart that helps us find the difference between two numbers without the calculation. All we have to do is trace the two numbers and find the difference in the point of intersection — It’s a convenient way to do simple subtraction.
The minuend (numbers we subtract from) is in the first row and subtrahend (numbers that subtract from the minuend) is in the first column — this arrangement can be switched.
Here’s how to read the subtraction table:
- We look at the minuend first, (here, it is in the first row)
- We look at the subtrahend which is in the first column
- We trace the point where both numbers meet to find the difference.
For instance, let’s find the result of 8 – 6 using the table:
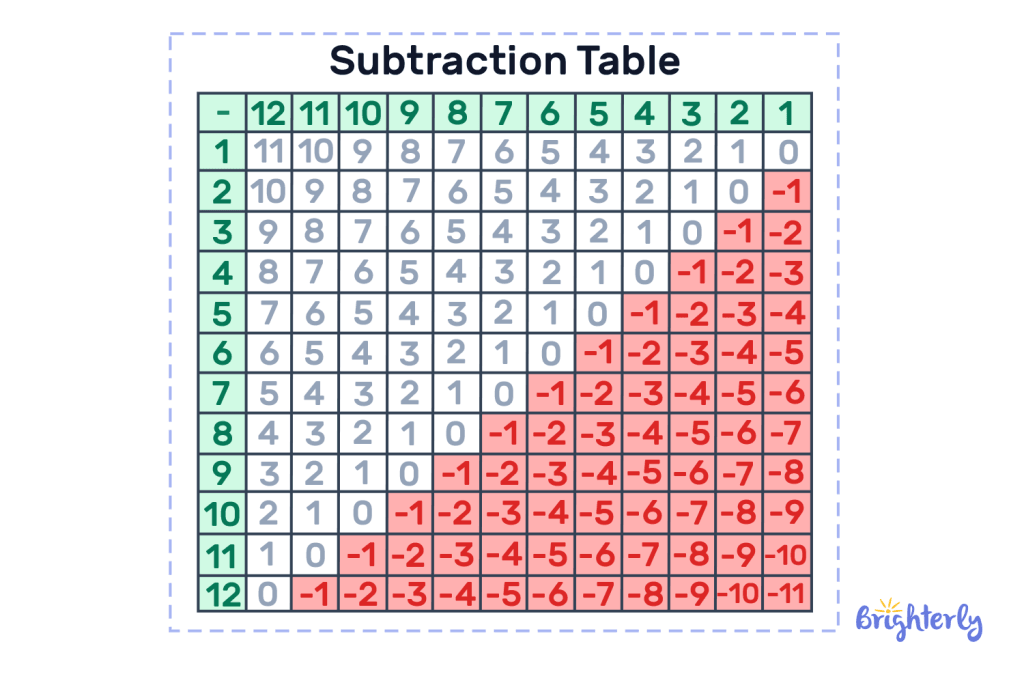
Per the chart, when we trace where 8 and 6 meet, the number is 2, meaning the difference is 2.
Subtraction Sums
We refer to math problems involving subtraction as subtraction sums. These include:
- Subtractions with regrouping
- Subtractions without regrouping
- Subtractions with word problems.
They also include simple subtractions between integers or more complex subtractions between fractions and decimals.
Subtraction of Fractions
We can subtract a fraction from another fraction and there are two ways to go about it:
Method 1: The denominator (the number below) is the same across the fractions, so we simply subtract the numerators (the numbers above). For example, 24/12 – 16/12. To solve this, we subtract 16 from 24 only, which gives us 8, without touching the denominator. Therefore, the answer is 8/12. We can also simplify it to 2./3.
Method 2: Here, the fractions don’t share a common denominator, so we have to find a common denominator for them before proceeding to subtract.
Subtraction of Integers
This is the most basic form of subtraction, however, it can be tricky. We know of subtracting positive whole numbers from each other. But what happens when we have to add between negative integers? Or subtract when the subtrahend has a larger value than the minuend?
To help with these types of problems, remember the following math rules:
- – + – = – (negative + negative = negative)
- – + + = – ( negative + positive = negative)
- – × + = – (negative × positive = negative)
- – × – = + (negative × negative = positive)
Therefore, if we have to add between two negative integers, the result will be negative, e.g., –3 + –3 = –6, and so on.
Also, if we subtract a larger number from a smaller number, the result will be negative. For instance, 12 – 13 = –1.
Subtraction on Number Line
A number line is a visual representation of numbers on a straight line and it can be a simple way to do subtraction without calculation.
We use the number line for subtraction by simply counting backward from the minuend. The number of times we count backward is the subtrahend.
Let’s illustrate with 6 – 4;
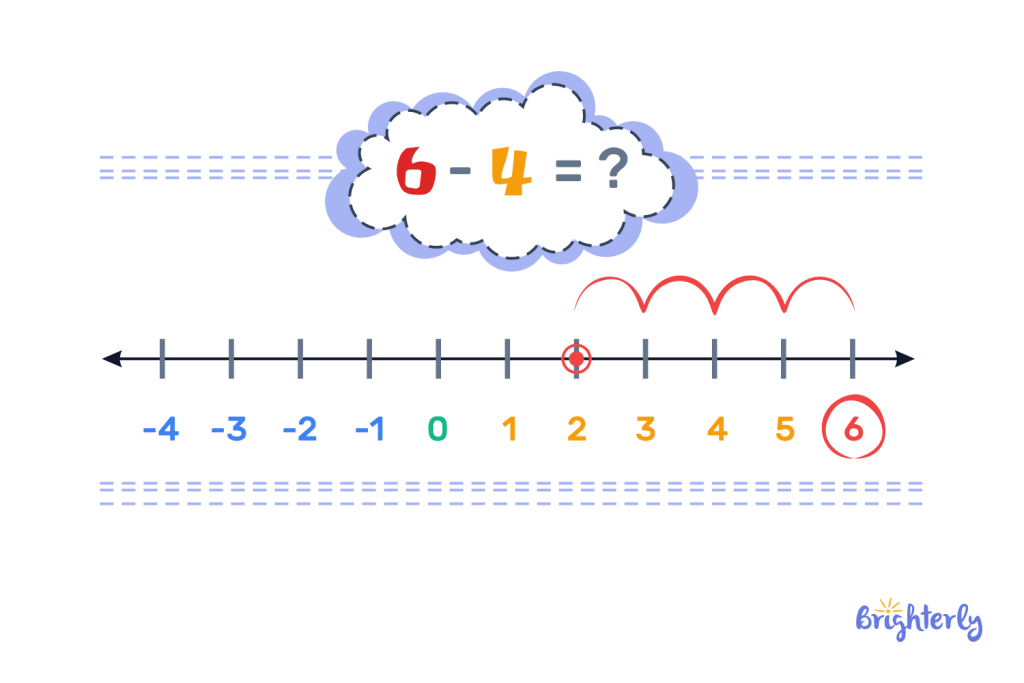
From the image, we first identified the minuend which is 6, and then counted backward 4 times which is the number of the subtrahend. The number we land upon (2) is the difference.
Subtraction Word Problems
Subtraction word problems are scenarios close to reality and can be solved with subtraction. For instance, Mark has 3 bars of chocolates and gives 1 bar to his friend, how many bars of chocolate is Mark left with?
This can be solved thus:
3 – 1 = 2.
Mark has 2 bars of chocolate.
Properties of Subtraction
Some basic rules guide how we solve equations involving subtractions. Here they are:
- Identity property of subtraction: When the subtrahend (the number we subtract from another number) is 0, the result will be the other number. For example, 3 – 0 = 3.
- Commutative property of subtraction: We cannot switch the places of the subtrahend and the minuend, to not affect the result. For instance 5 – 3 and 3 – 5 are not the same equation and will give different answers.
- Distributive property of subtraction: If we multiply c after we subtract a from b, the result is the same if we multiply a by c and b by c, then multiply.
This means 3 × (4 – 2) = 3 × 4 – 3 × 2
3 × (2 ) = 12 – 6
6 = 6
- Inverse property of subtraction: A number subtracted from itself will be 0.
For example, 8 – 8 = 0.
- Subtraction property of equality: if we subtract an equation, with the same non-zero number, the resulting equation will remain balanced.
For example, y – 6 = 4.
y – 6 – 10 = 4 – 10
y –16 = –6.
Solved Examples On Subtraction
Solved math problem 1
Jim is asked to share a jar of 12 cookies. He gives Amber 4 cookies and Milo 3 cookies. How many cookies is he left with?
Answer
12 – 4 –3 = 5
| Jim is left with 5 cookies. |
Solved math problem 2
Mel buys 8 crayons. He gives 4 to his friends and 2 to his teacher. How many crayons is he left with?
Answer
8 – 4 – 2 = 2
| Mel is left with 2 crayons. |
Practice Problems On Subtraction
Subtraction: worksheets
The experts at Brighterly have curated a list of free worksheets on subtraction to help young learners get more familiar with the topic:
- Subtraction worksheets
- Subtraction word problem worksheets
- Adding and subtracting negative numbers worksheets
Frequently Asked Questions On Subtraction
What is subtraction?
Subtraction definition in math is the mathematical process of removing a quantity from another quantity or finding the difference between two quantities.
What is the symbol for subtraction?
“–” is the symbol of subtraction. The subtract symbol is also known as the minus sign. it is placed between the numbers we intend to find their difference.
What is the formula for subtraction?
Minuend – Subtrahend = Difference is the formula for subtraction. The minuend is the number that we subtract from, the subtrahend is the number that subtracts from the minuend, and the difference is the result.
What are subtraction facts?
Subtraction math facts are memorizable short calculations that aid quicker subtraction mastery. Some of them are 7 – 5 = 2, 10 – 4 = 6, 8 – 2 = 6, etc.