Transformation Geometry – Definition with Examples
Updated on November 27, 2025
Are you ready to explore the world of geometry and become a master of the subject? Well, you are in the right place! At Brighterly, we provide a lot of informative articles on different topics in geometry and math to help you improve your knowledge and grades.
Today, we are going to cover transformation geometry. Transformations in geometry are changes we can make to geometric shapes on a coordinate plane that result in different dimensions or positions.
Here, we are going to cover what is a transformation in math, the different types of transformations, and the rules attached to them. We’ll also provide some transformation examples, then give you some practice test questions so you can apply your newfound knowledge.
What are transformations in geometry?
The transformation definition math is changes we can make to geometric shapes like triangles, squares, circles, and more — also known as figures — on a coordinate plane.
These transformations change different aspects of shapes, such as their size or position. Some transformations are rigid transformations, meaning the shape and size of your figure stay the same. Others are non-rigid, meaning these features of your figure will change.
Types of transformations
There are five key types of transformation that we’ll cover in this article:
- Transformation of translation
- Transformation of quadratic functions
- Transformation of reflection
- Transformation of rotation
- Transformation of dilation
Each type of transformation has a different set of geometry transformation rules and a different effect on our figures.
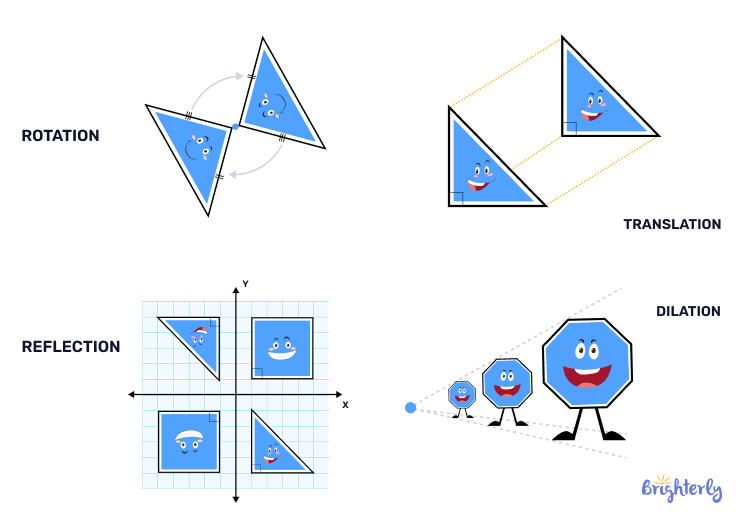
Rules for transformations
Every type of transformation has a specific set of rules that dictate the changes that it makes to our figures. These changes can include their size, shape, or position. We’re going to explain everything you need to know about the individual transformations in geometry rules below.
Transformation of translation
Translation is a type of transformation that changes the position of a figure without changing its shape or size. This makes it a rigid transformation — i.e., a transformation that does not fundamentally alter the figure’s dimensions or shape. Once you have translated your figure, it will appear the same, but it will be in a different position on your coordinate plane.
Transformation of quadratic functions
The transformation of quadratic functions is a little different from other types of transformation, because in it, we’re working with a quadratic equation that has been graphed on a coordinate plane rather than a defined shape.
The transformation of quadratic functions changes the shape or position of the quadratic functions that have been graphed on a grid. These transformations in geometry are non-rigid because they can change the shape and size of a graph. Thus, the shapes can be translated, reflected, rotated, and undergo vertical or horizontal changes.
Transformation of reflection
The transformation of reflection essentially produces a mirror image of your figure. Your figure is flipped over an axis, so you see it in reverse. Reflection is a rigid transformation in geometry because, although your image is flipped, its size and shape remain the same. To remember the transformation of reflection, just think about your figure as mirrored exactly.
Transformation of rotation
When a figure is transformed through rotation, it is rotated to a different position from a specific point — aka the center of rotation. This is another type of rigid transformations math, because rotating an image around its center of rotation does not change its shape or size. One point on the shape will remain in the same place on your coordinate plane, while the rest of the shape will be in a new position and have new coordinates.
Transformation of dilation
Dilating an image makes it larger or smaller, while keeping it in proportion. An easy way to remember this is to think about how your pupils dilate in the light or dark — they get larger or smaller depending on how much light reaches your eyes. Unlike many other forms of transformation we have covered so far, this is a non-rigid transformation in geometry, because the size of the image is altered.
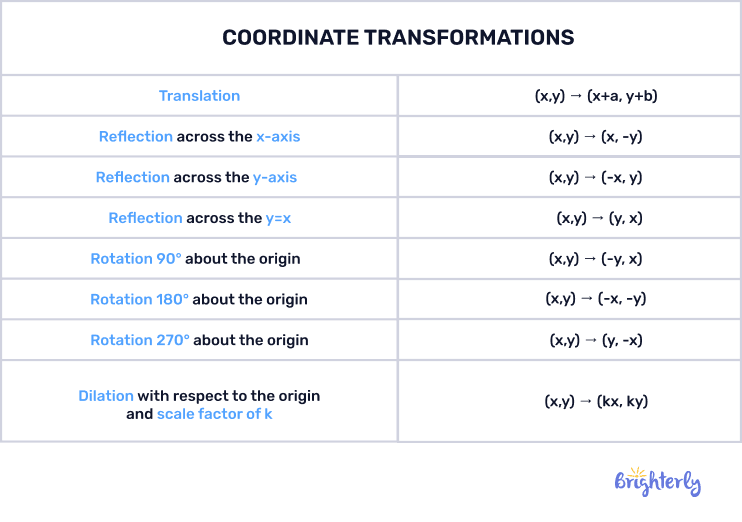
Transformation formula
As well as transformation rules in geometry, each transformation has its own unique formula that dictates how your figure is transformed across your coordinate plane. Here is each individual transformation’s formula, depending on how exactly you transform it. You’ll notice that you can transform figures across different axes, horizontally and vertically, and clockwise or counterclockwise:
- Translation
- Horizontal: (x, y) → (x + k, y)
- Vertical: (x, y) → (x, y + j)
- Quadratic functions:
- Reflection
- Over x axis: (x, y) → (x, -y)
- Over y axis: (x, y) → (y, -x)
- Rotation
- 90° clockwise: (x, y) → (y, -x)
- 90 counterclockwise: (x, y) → (-y, x)
- 180: (x, y) → (-x, -y)
- 270 clockwise: (x, y) → (-y, x)
- 270 counterclockwise: (x, y) → (y, -x)
- 360:(x, y) → (y, x)
- Dilation: (x, y) → (kx, ky)
Examples of transformations
There are lots of examples of transformations in the world around us. If you look in a mirror, for a transformation example, you see a reflection of yourself. You can replicate this in math class by drawing a figure on a coordinate plane, then holding a mirror to it. This will produce the same effect as using the transformations formulas to transform it.
If we look at something like translation, moving an item in your bedroom or on your classroom table could be considered a translation. You are simply moving the item to a different space, but you are not changing the shape or size of it.
Rotation can be seen when we flip an object around, keeping one edge or corner in place. For example, if you place a protractor on a piece of paper and hold one of its corners in the same place as you rotate it, that is a rotation transformation!
Finally, the best example of dilation is the way our pupils dilate. In order to let more light in, our pupils will enlarge — but they will stay the same shape. That’s why this transformation is called dilation — because it does the same thing.
Practice questions on geometry transformations
Now, are you ready to try out some practice questions on transformational geometry? These questions will help you understand how to apply the knowledge you have gained in this article to questions on geometric transformations.
- Translate the point (3, 5) by 3 units down and 5 units to the right. What are the coordinates of the new position of the point?
- Rotate the point (3, 3) 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin. Describe the transformation and explain where the point lands.
- A square has a side length of 3 units. If the square is dilated by a factor of 2, what is the length of the sides of the new square?
Conclusion
Here, we have covered the transformation geometry definition, explained each type of transformation, and provided you with some examples and practice questions. Now, you know all there is to know about transformations math!
Transformations are an important concept that helps you understand how shapes change and move on a coordinate plane, and knowing this information opens up the door to more complex geometrical concepts, like congruence, pattern spotting, and spatial reasoning. This knowledge will set you up for a successful journey in math.
Frequently asked questions on transformations geometry
What is a transformation in geometry?
A transformation in geometry is the change we make to a figure on a coordinate plane. We can change its position, size, or shape. Transformations can either be rigid (they don’t change the size and shape of our figure) or non-rigid (they do change its shape and size).
What are the four types of transformations?
The four main types of transformation are:
- Transformation of translation
- Transformation of rotation
- Transformation of reflection
- Transformation of dilation
We can also transform quadratic functions that are expressed as graphs on a coordinate plane, which we’d consider the fifth type of transformation, but it’s a little different.
What are transformation rules?
Transformation rules geometry are guidelines on how we transform a figure. Each different transformation has different rules. For example, the transformation of reflection means that flipping the figure results in a reflection, i.e., the same shape but in reverse.
What is a real life example of geometric transformation?
The transformation geometry examples in real life include looking into a clear lake and seeing a reflection of yourself. Moving an object from one place to another is a translation, and turning an object like a ruler on its axis is a reflection.






