How to Retain Information: Help Kids Retain Knowledge After Class
reviewed by Franz Jerby Delos Santos
Updated on February 16, 2026
Wonder how much of what your kid learned during classes they’d forget by the end of the year? It all depends on memory retention, applied strategies, and practice.
Stay with me to explore how to retain information and discover 10 useful ways to make learning stick.
Key points:
- Absorbing information may be difficult for kids due to a lack of personal connection, engagement, and focus, as well as cognitive overload and specific learning needs.
- The best ways to improve information retention are via active recall of knowledge, practice, meaningful learning, and regular reviews.
- To actively recall information, kids should resort to flashcards, notes, worksheets, quizzes, and teaching others.
- Spaced repetition techniques are crucial to counter forgetting and support long-term knowledge retention.
- Multisensory and experience-based learning allows making lessons memorable and meaningful for kids.
What is information retention?
Information retention refers to the cognitive process by which students maintain information in their memory. Scientifically, it is possible, as the student’s brain forms neural connections when engaging with new information.
During information retention, children first encode the data, store it, and then retrieve it.
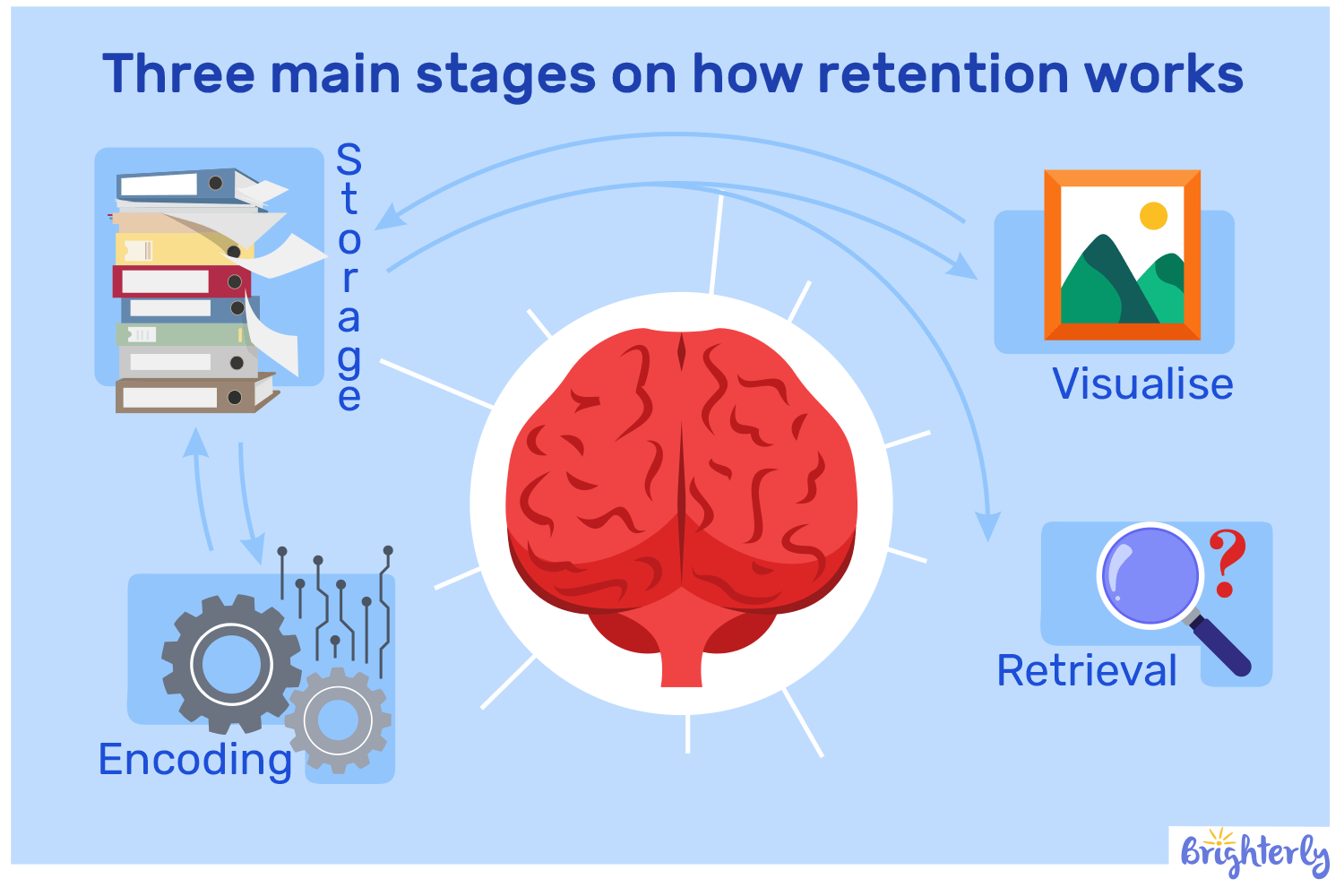
Without these stages, a student won’t be able to form new memories and create strong neural connections with knowledge.
Key aspects of information retention include:
- Engagement. The more a kid engages with information, the better they will retain it.
- Relevance and personal connection. A kid is more likely to remember topics or information that is relevant to their interests or hobbies.
- Cognitive load. The overload with information can be overwhelming and bring confusion, preventing the retention of knowledge.
- Focus and environment. If a kid has no distractions, they can better concentrate on topics and have clearer connections.
Why is retaining information so difficult for kids?
The reasons why retaining information is difficult can vary from kid to kid, but they can include the learning environment, overload with information, kids’ learning needs and style, or factors that don’t belong to school or the learning process, like stress levels or tiredness.
If the learning environment is full of distractions, then it will be difficult for kids to retain information. Besides, certain strategies, like passive learning, won’t work if they don’t suit students’ learning styles.
Note: A study by NASET underlines that ADHD students struggle with information retention because of a deficit that affects working memory and information processing.
Key reasons for difficulty in information retention:
- The speed of information processing. It affects how a kid connects new facts to what they already know.
- Lack of motivation and interest. Kids may simply see no reward in learning new information.
- Attention and distractions. If there is no focus, it decreases the capacity of a kid to absorb new facts, thus, recall them properly.
- Learning needs or disabilities. Kids may need specific strategies or more time to process certain information.
What is the best way to retain information?
The best way to study and retain information is through active engagement, the use of materials, and regular review. Besides, learning should be meaningful for a learner for information to stick.
Moreover, such a combination works even better if backed by spaced repetition. If a student combines active recall and repeated practice with short breaks, the learning will stick in long-term memory.
Best ways to retain information after class
- Expert tutoring
- Worksheets and tests
- Spaced repetition
- Turning knowledge into experience
- Mapping and note-taking
- Teaching others or reproducing information
- Making topics personal and interesting
- Mnemonics techniques and tools
- Avoiding distractions
- Multisensory learning
Note: To improve knowledge retention of a kid, combine these strategies as they allow processing information and skills via different systems
How to retain information with tutoring
Resorting to a tutor is a pretty universal approach that parents commonly use. That’s because:
- Working with an expert tutor offers personalization, allowing you to spot weak areas and receive interventions or extra practice.
- One-on-one focus means more engagement and increased attention to learning needs and challenges.
- With the right tutor, a kid gets support and motivation that suits their learning style.
As a result, kids get targeted practice within a learning-oriented environment. However, such an approach depends on a tutor and won’t develop independent learners.
How Brighterly helps kids with information retention
A place where you can get solid and certified tutoring support is Brighterly math and reading platform.
Brighterly is known for its personalized, adaptive tutoring for K-12 students.
- For instance, if a kid can’t retain information because passive learning works poorly, Brighterly tutors will prioritize interactive games or apply storytelling.
- If there’s an overload or significant stress, they will adjust the pace of learning without sacrificing the goals of the program.
That way, each reading and math program can be customized to specific topics or styles while still following national standards.
Retain information via practice and review
When kids do tasks on newly obtained information, it makes their brains get the information out of the memory, strengthening the neural pathways related to this piece of knowledge.
Note: The research by Henry Roediger and Jeffrey Karpicke shows that students who did tests retained around 80% of information after a week, while those who used passive recalling techniques retained less than 35%.
Besides, during practice, you and your kid see the areas that need recalling or revising, call it feedback on absorbing information and its use.
Using flashcards, worksheets, and other techniques
As practice and tests can be boring and overwhelming for a kid, try making it engaging, interactive, game-like, but a bit challenging.
- Use flashcards with questions and answers on different sides of them; resort to digital tools like Quizlet for it.
- Use worksheets and tests on a variety of topics, from math to reading.
- Ask simple or tricky questions based on the info in a chapter or a novel.
- Use the blank page or the blurting technique to ask a child to write what they know from memory.
- Do funny quizzes in turns with a kid and transform this practice into a competition.
Note: Brighterly provides very interactive math and reading worksheets that differ by grade, as well as math and reading tests that you can use to identify gaps or practice key concepts.
Use spaced repetition
Often, kids are unable to retain information in the long run because of the forgetting curve, the concept describing how the new knowledge fades away.
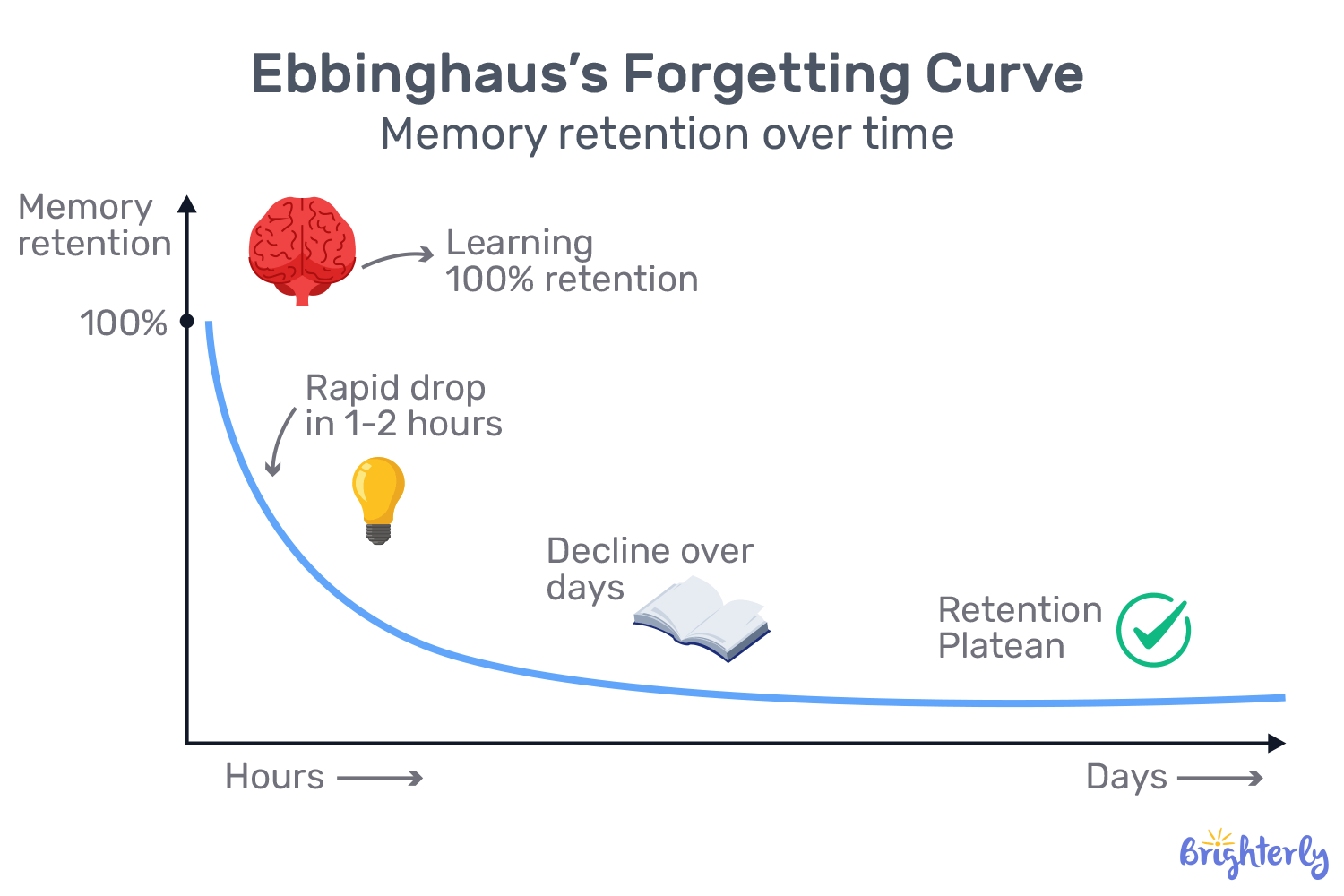
The forgetting, or “Ebbinghaus,” curve assumes that students forget information very quickly (the older they are, the quicker), up to 2/3 during the first day (as shown by the Ch. Sterling research).
There, spaced repetition is a key strategy to counteract forgetting, or working memory decay. That’s why every class usually starts with a review of materials; it helps to prevent forgetting in the long run.
What are the best spaced repetition strategies?
- Use a spacing schedule or 2/3/7 method. On the first day, a kid learns the material, on the 2, 3, and 7th day, they review the materials.
- Make a calendar of reviews. You can schedule review sessions for your kid on different topics.
- Combine reviews with practice and tests. You can also use flashcards or the blurting method.
- Make repetition a daily routine. Incorporate small practice pieces into kids’ daily routine.
Absorbing information via experience
Another way for kids to retain information better is by turning knowledge into experience. It works because kids learn best by doing and creating personal connections.
Although exact percentages vary by study, the learning pyramid concept suggests that students retain 75% of what they learn through active participation and such experiences as experiments, and only 10% from reading.
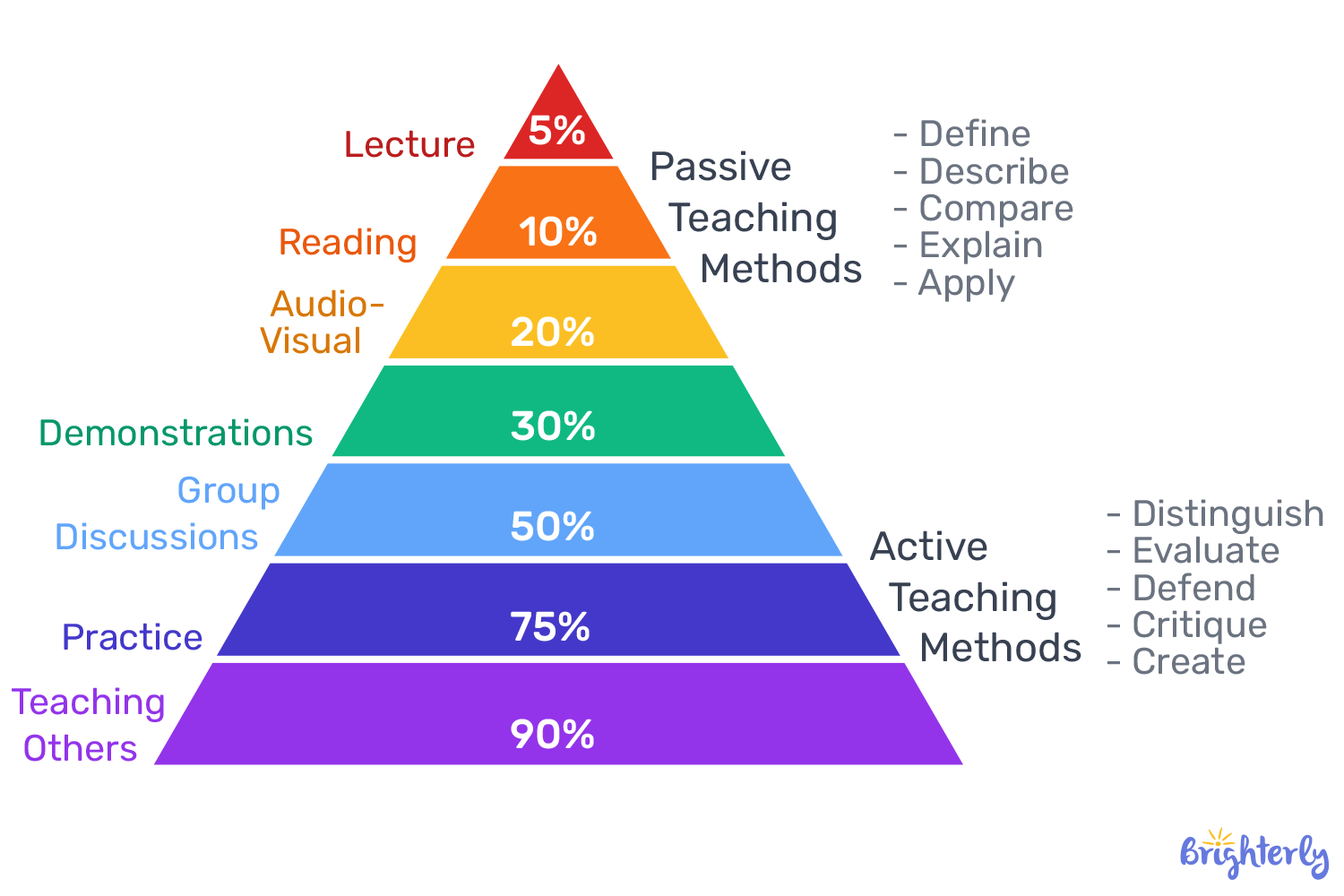
So, what are great ways for retention improvement?
- After a class on science, try simple water experiments at home.
- When learning fractions, cook together with a kid to show how ingredients double.
- After studying a concept, try a project or a game around it.
Note: In particular, the research conducted by Taryn Bauerle & Travis D. Park shows that experiential learning can significantly improve retention rates in plant sciences.
Improve knowledge retention via mapping and note-taking
You already know that the first day is crucial for remembering new topics. Thus, reinforce the learning with visual notes, maps, and bullet lists during or after the class. They are great tools to help the brain organize information.
What to do after studying to retain information?
- Review notes by explaining them out loud after a lesson.
- Apply visualization techniques like infographics and diagrams, or concept maps.
- Use analogies and drawings to relate concepts to real life.
- Apply specific methods like Cornell notes.
Ask them to teach someone to improve retention
Another exciting method refers to the protégé effect, contemplating that a student can learn something better while sharing materials or teaching others.

Under it, a kid will need to organize, store, and properly understand the information before retelling it. That way, a child can make deeper connections with the topic once they reproduce the knowledge.
How to help kids practice teaching to retain information?
- Ask kids to teach the topics back to the group, a friend, or a family member; try the Jigsaw method or the Feynman technique.
- Turn teaching into a play, ask kids to educate their favorite toys or characters.
- Let them use multimedia, boards, and notes; ask questions to close gaps.
Note: If your kid finds it hard to teach, perform elaborative interrogation with “why” questions, or ask them to reflect on a certain fact, it will also form connections.
Make learning personal
Have you ever asked yourself, “Why do I struggle to retain information or a specific topic?” I bet you do, and in many cases, the reason was that it was outside your area of interest.
It’s all because personal connections make learning meaningful and thus memorable. Moreover, the emotional engagement with the material helps to store facts more effectively and ensure better encoding.
How to relate lessons to your kids’ interests?
- You can turn math problems into game scenarios for their favorite characters.
- If kids love music, you can set facts to a tune.
- Use relational learning and explain concepts with analogies or examples that kids recognize.
Use mnemonic devices to boost retention of information
Children do find it hard to retain information without some aid. That’s why you should use mnemonic devices. They are aids that help strengthen memory via associations and fun.
For example, you can link cartoons to math concepts, turn rote exercises into something imaginative, or make silly phrases to memorize formulas.

What are the mnemonics to consider?
- For kids in elementary school, use rhymes, colorful drawings, gestures, alphabet songs, and acronyms.
- For middle school kids, develop acronyms, short stories, and mind maps.
- For high school kids, try advanced acronyms, build memory palaces, analogies, and symbols.
Avoid distractions
Next, to ensure that your kid retains information after class, think of eliminating distractions. It’s important to have an adequate environment, routine, and habits. They are to add focus, discipline, and decrease cognitive load.
How to retain information when studying and keep focus?
- Set up clean and quiet study spots.
- Avoid overload, ensure kids focus on one task at a time, followed by breaks.
- Try microlearning sessions.
- Help kids with their study routine, including calendars, task lists, and even rewards.
Note: Student mental health can affect the ability to retain information, particularly due to information fatigue or stress.
Apply multisensory learning
Lastly, appealing to different senses while learning is another way to boost knowledge retention. Why? It appeals to different learning systems, styles, and needs simultaneously.

What are the multisensory learning examples?
- Using objects and hands-on manipulatives to explain math concepts.
- Building models with blocks as projects or practice.
- Recording your notes and reviewing them.
- Creating mind maps using colors and images.
- Integrating educational videos and audio learning tools.
Note: Multi-sensory strategies are about mixing visual, auditory, and kinesthetic techniques to create more diverse and deep connections.
How to retain information for a test?
The best way to retain information for a test is to combine classic methods, including flashcards and reviewing notes, and modern ones like visual aids, concept maps, and back them with a spacing schedule or a calendar of review.
That way, your kid will be able to prepare thoroughly and reduce overload and stress.
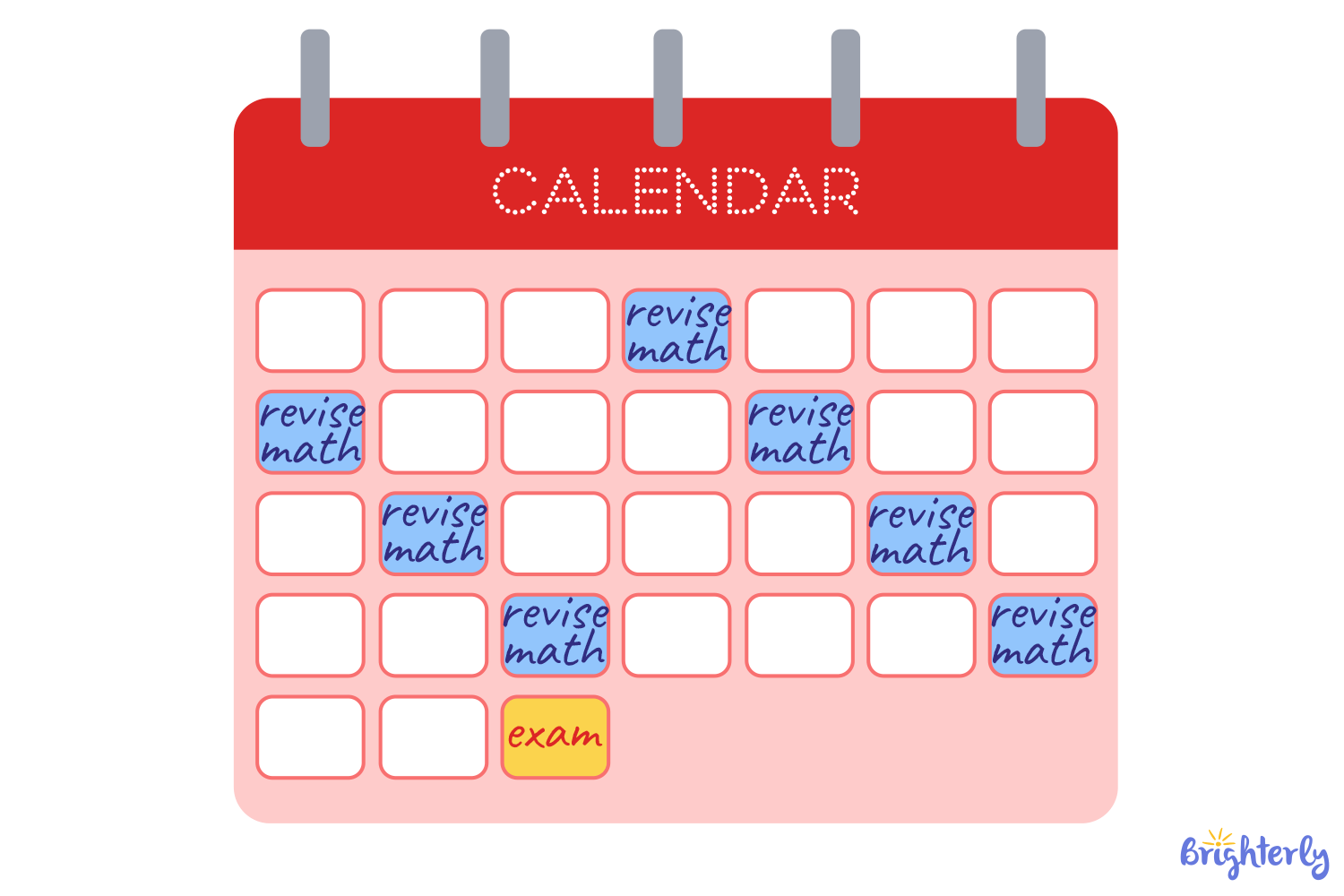
What are specific tips in this regard?
- Start early so kids don’t cram, instead plan short reviews days before the test to improve knowledge retention.
- Have notes and facts in one place, revisit them, and do tests to identify gaps.
- Try microlearning to prepare and prevent overload.
- The most effective recall techniques are flashcards and retelling or teaching concepts to others.
Note: Make sure a kid eats well while preparing, as the 2008 study by Katharina Widenhorn-Müller shows that skipping breakfast can negatively affect the cognitive performance of kids.
How to retain information when listening?
To retain information when listening, a student should engage actively with the information or speaker, make notes, ask or write questions, and look up the concepts used.

If possible, a child can use analogies, associations, or drawings to note information. It will allow them to connect with them later and recall materials.
Besides, a good piece of advice is to make information meaningful to a kid, so that they are interested in the topic or its application.
Note: According to the Learning Pyramid model, students often retain 20% of what they hear if not supported by specific strategies.
How to retain information with ADHD
For children with ADHD, the retention of knowledge requires extra structure, movement, and management of attention. The main reason is that students with ADHD may feel that they are unable to retain information because their focus drifts.
According to the article on ADHD statistics, ADHD usually comes together with other difficulties like anxiety or depression. Thus, it’s important to keep calm, take a positive approach, and consider kids’ preferences.
Here are some quick tips on how to help ADHD students retain information:
- Make learning funny, scary, or odd; use emotions, stories, and analogies to make it engaging.
- Use visual schedules and timers to separate tasks.
- Offer kids the opportunity to study different subjects in different places.
- Clap out math problems and use hand signals for spelling (for younger students)
- Do movement breaks between studying, they may involve squeezing a ball, jumping, walking, or spinning.
Note: Show your kid the Method of Loci, or its vatiation the Classroom Visualization, under which kids connect specific places in the classroom to certain information and use it for the retrieval of facts during a test.
Final study tips to help kids retain information
If you want to help your kids strengthen their memory, you don’t need complicated systems or tricky approaches. What it takes is ensuring consistency, active practice, spaced repetition, and a proper environment. Besides, you think of making learning meaningful and engaging.
At the same time, offer room for practice, teaching others, and application of knowledge in real life. They will help connect to learning on a deeper level.
If you feel that your kid loses confidence, is overloaded, or needs learning to match preferences, why not personalize the lessons so that topics stick? Book free lesson to try Brighterly tutoring!