Volume – Definition, Formula, Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on October 8, 2024
At Brighterly, we’re committed to teaching kids about core math concepts in a way that’s enjoyable and easy to understand.
As your kids are introduced to 3D shapes, they’ll be introduced to volume in math. We’ve put together everything you need to know about volume here.
We’ll cover the volume definition and its formulae, give real examples and share practice questions.
What is volume?
Volume in math relates specifically to 3D subjects. It refers to how much space is available within a 3D shape. It’s essential to understand the relationships between spaces and sizes, as well as understand the constraints of containers and how they fit liquids into them. We’ve included the volume math definition below.
Volume definition
The volume definition is the total amount of space within a 3D shape and how much liquid or other material could fit into it. There are specific measurements for volume in math, which are usually milliliters, liters, gallons, cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³).
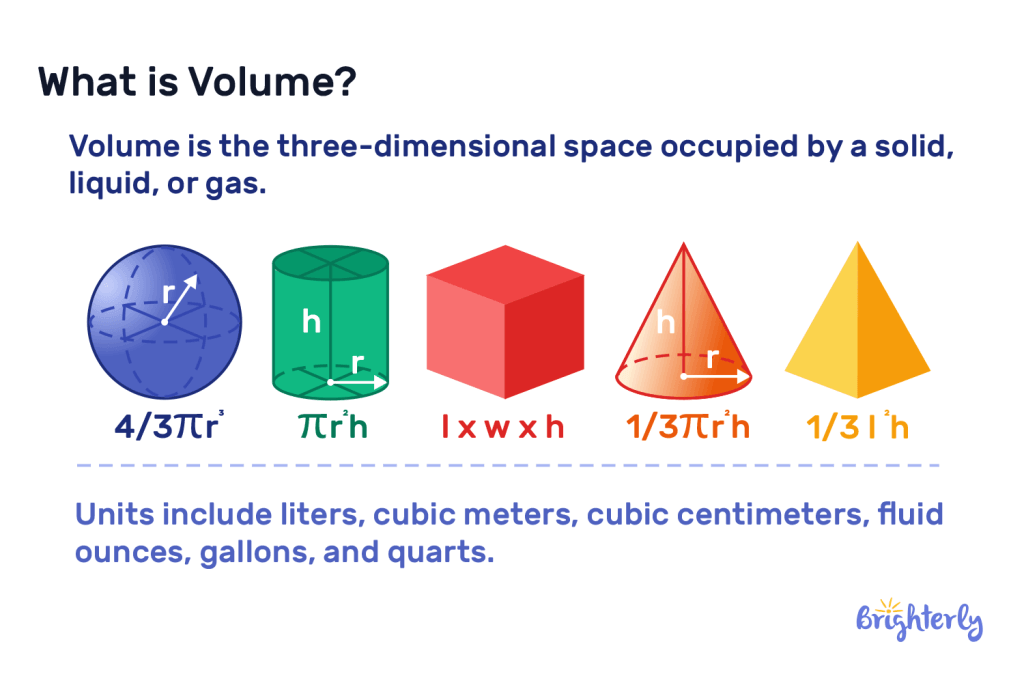
Volume of 3D shapes
The volume of 3D shapes is calculated differently depending on the type of 3D shape. You won’t measure the volume of a sphere in the same way you’d measure the volume of a cube. Here, we cover some of the most common 3D shapes and how to calculate their formula.
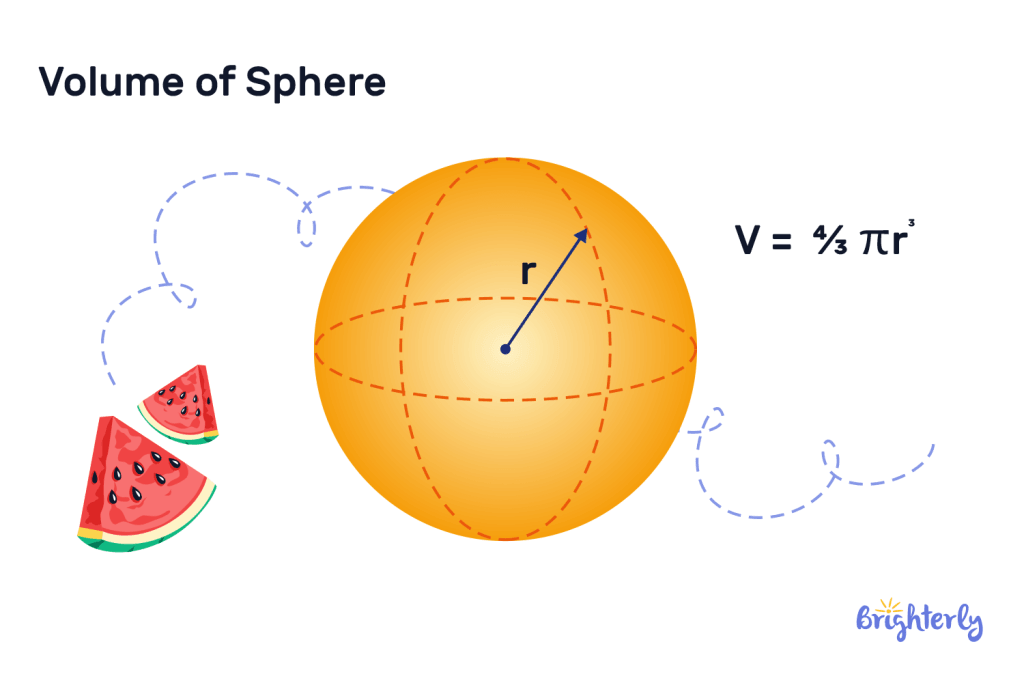
Sphere
Spheres are characterized by being perfectly round in every direction – a ball is an example of a sphere. Finding the volume of a sphere requires using the following formula:
Volume = (4/3) × π × radius3
In this volume formula, radius represents the distance from the surface of the sphere to its center.
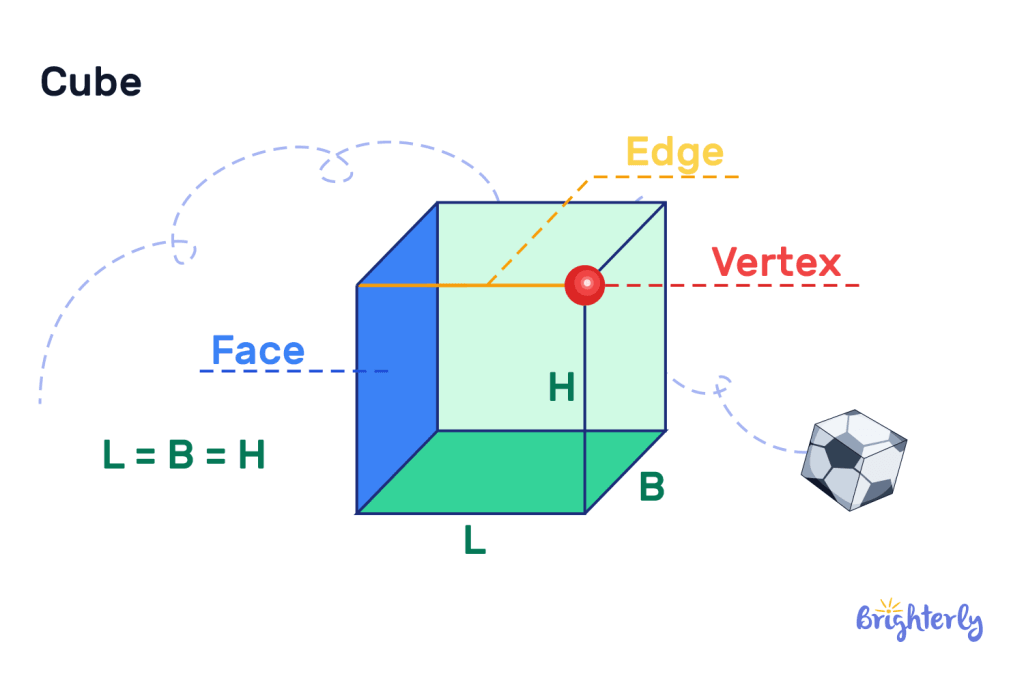
Cube
Cubes have six equal-sized square faces, representing the 3D version of an equal-sided square. Finding the volume of a cube requires using the following formula:
Volume = side3
In this volume formula, the “side” refers to the length of any of the cube’s equal sides.
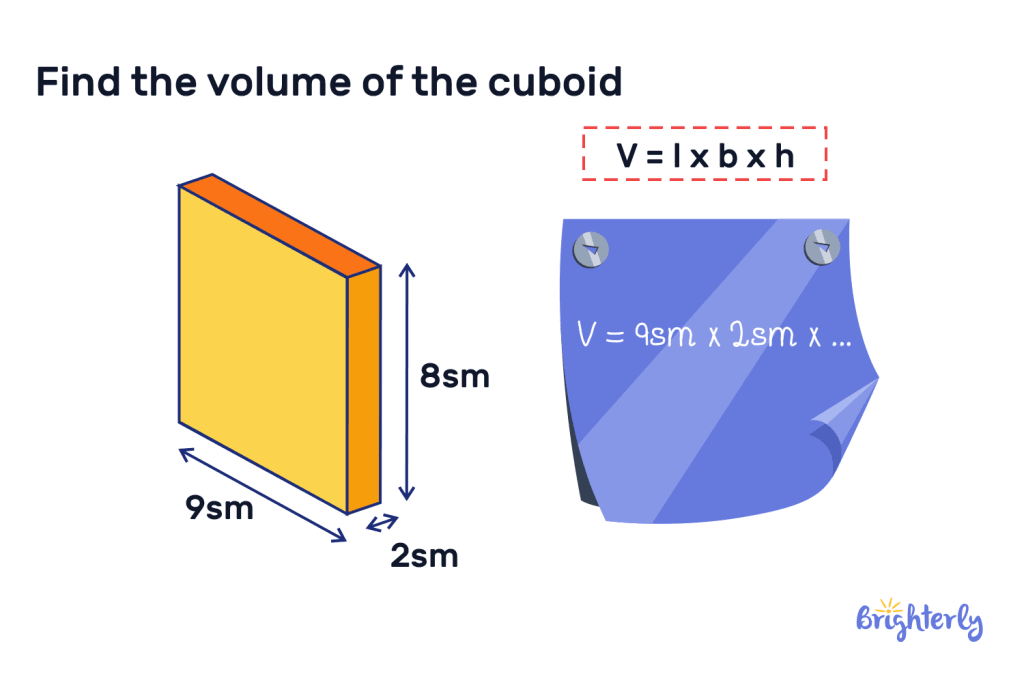
Cuboid
A cuboid has six rectangular faces that do not all have to be equal, but the opposite faces are equal. Finding the volume of a cuboid requires using the following formula:
Volume of a cuboid = l × b × h
In this volume formula, l = length. b = breadth. h = height.
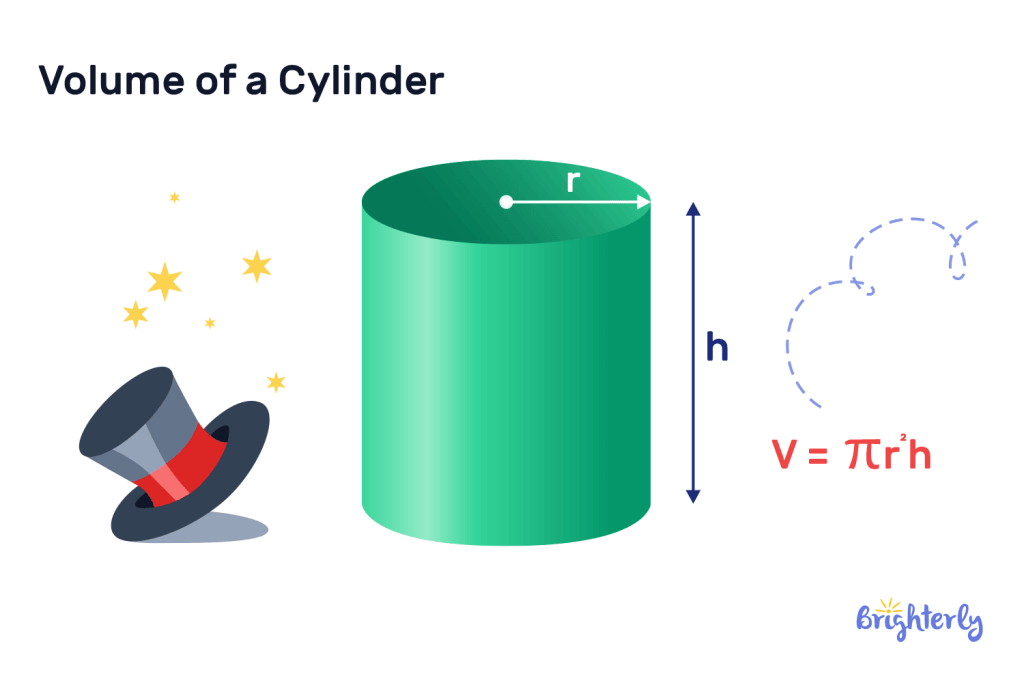
Cylinder
The 3D shape of a cylinder has a round curved surface connected by two circular bases. Finding the volume of a cylinder requires using the following formula:
Volume = π × radius2 × height
In this volume formula, “radius” is the length from the edge of the circular base to the center of the circular base. The “height” represents the length between the two bases.
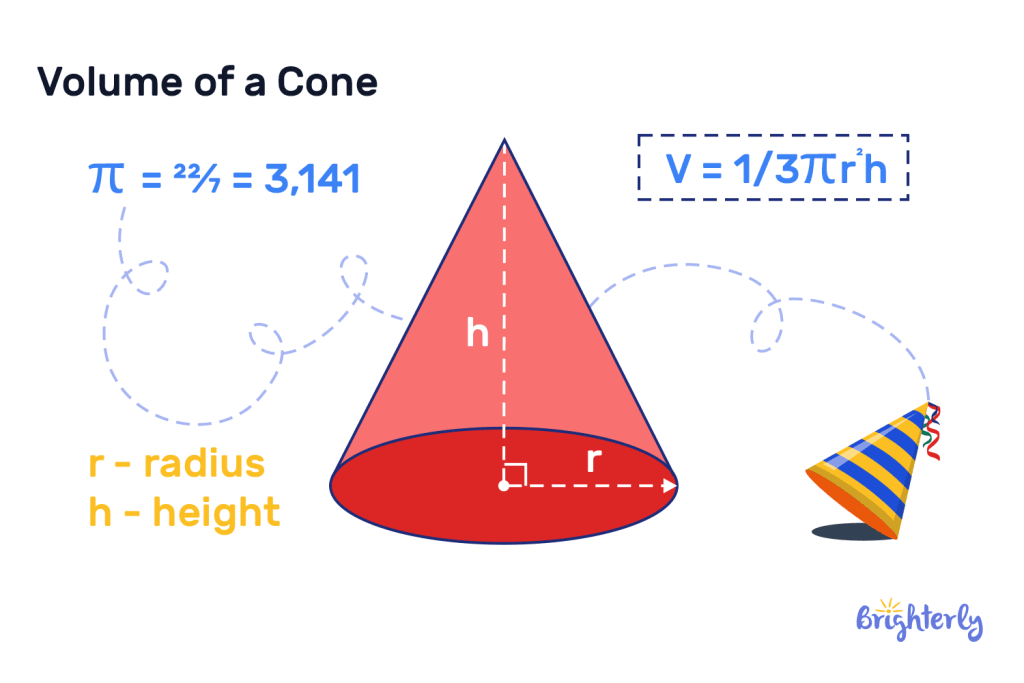
Cone
Cones are defined as 3D shapes that have a curved surface that narrows to a point (the vertex), plus a circular base. Finding the volume of a cone requires using the following formula:
Volume = (1/3) × π × radius2 × height
In this volume formula, “radius” is the length between the edge of the circular base to the center of it. The “height” is the distance between the base and the vertex.
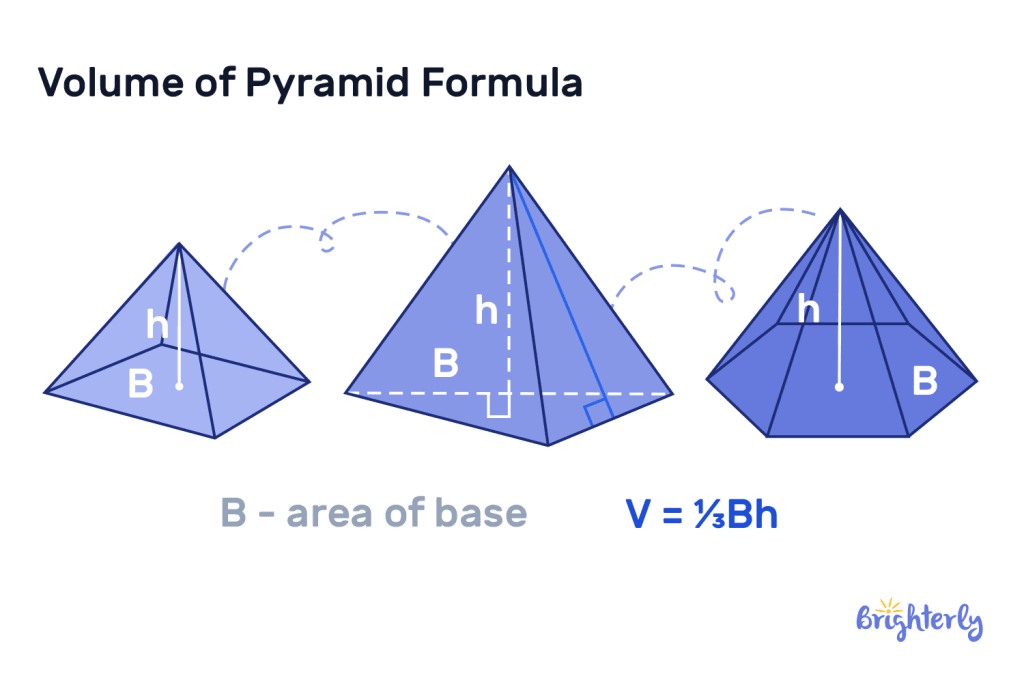
Pyramid
This 3D polyhedron has triangular sides that meet at a point (the apex), plus a polygonal base. Finding the volume of a pyramid requires using the following formula:
Volume = (1/3) × base area × height
In this volume formula, the “base area” represents the polygonal base area. The “height” represents the perpendicular distance from the base to the apex.
How to calculate the volume?
To calculate the volume of a 3D shape or container, there are some steps you need to take. Here’s how to calculate the volume of a 3D shape or container.
- Identify what the container or shape is – i.e. a sphere, cube, cuboid, etc.
- Understand what the relevant dimensions are for the container or shape (e.g. radius, base area, height or side length).
- Use the relevant shape volume formula.
- Replace the placeholders in the formula with the relevant dimensions and calculate the volume formula.
- Use the right unit of measurement in your result (e.g., gallons, liters, cubic centimeters or cubic meters).
List of volume formulas
Here is a list of volume formulas for the most common types of 3D shapes for quick reference:
- Cube: volume = side3
- Cylinder: volume = π × radius2 × height
- Pyramid: volume = (1/3) × base area × height
- Cone: volume = (1/3) × π × radius2 × height
- Sphere: volume = (4/3) × π × radius3
Solved math tasks: examples
Here, we’ve included some finding volume practice problems that will help your kid improve their knowledge.
Solved math task 1
What is the volume of a cylinder that has a radius of 3cm and a height of 5cm?
Answer:
| 141 cubic centimeters |
Volume = π × radius2 × height
Volume = π × (32) × 5
Volume ≈ 141.37 cubic centimeters
Solved math task 2
What is the volume of a cube with a side length of 4cm?
Answer:
| 64 cubic centimeters |
Volume = side3
Volume = 43
Volume = 64 cubic centimeters
Volume: practice math problems
Volume worksheets
Brighterly offers a range of math worksheets on volume in math and 3D shapes for you to put your knowledge to the test and improve your understanding of volume.