Reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
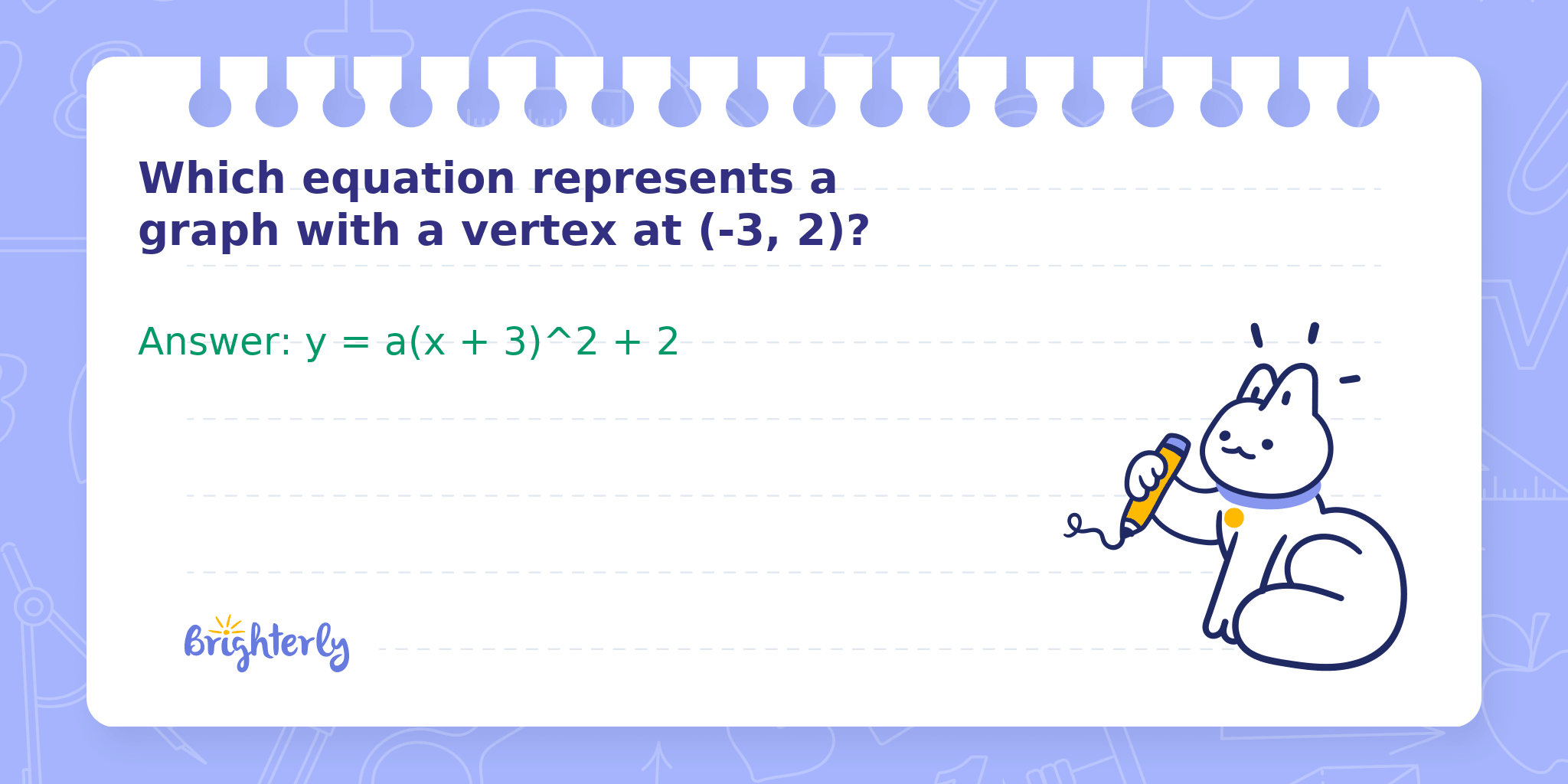
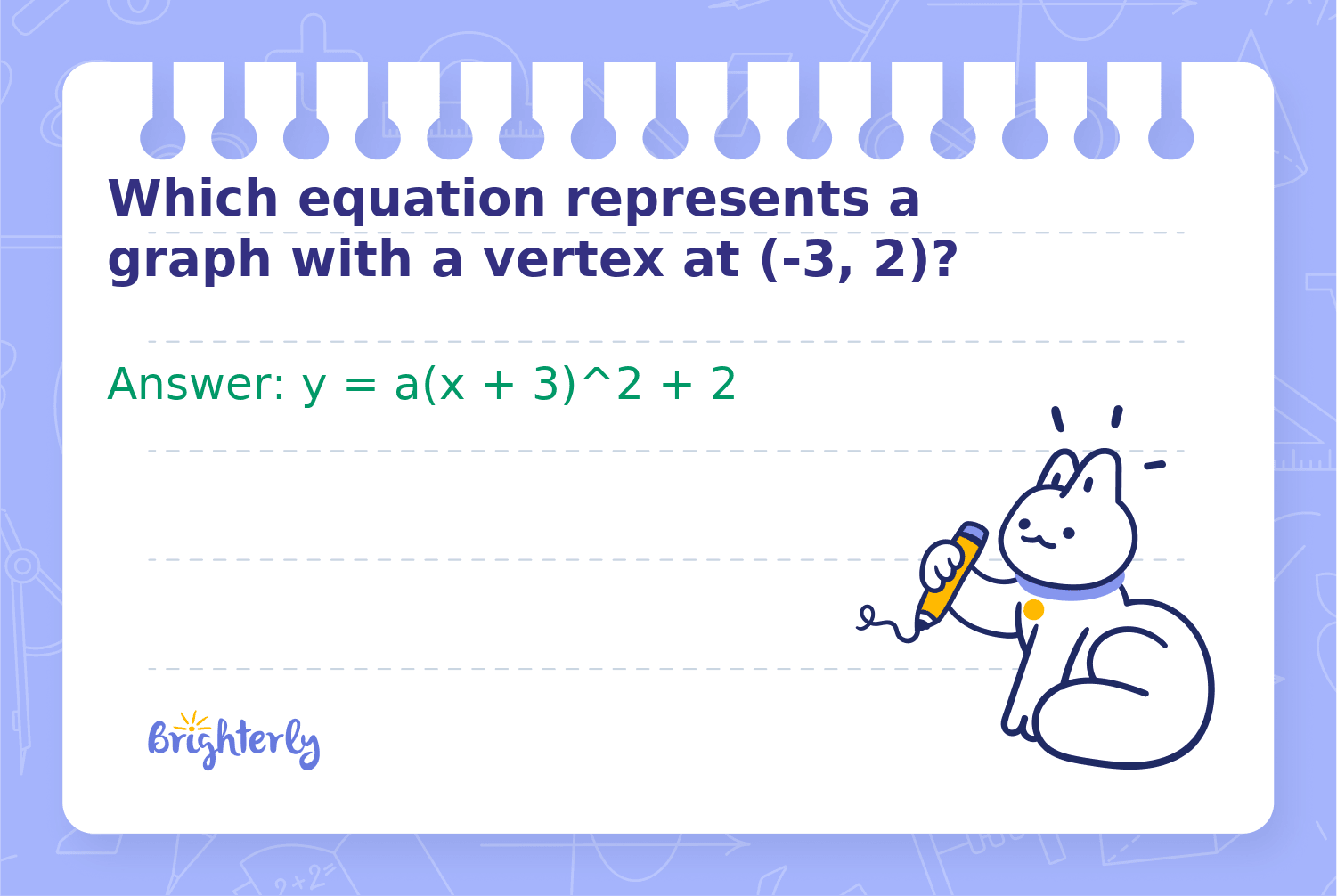
Which equation represents a graph with a vertex at (-3, 2)?
Answer: y = a(x + 3)^2 + 2
The equation of a parabola in vertex form highlights the location of its vertex directly. For a parabola, this is usually expressed as y = a(x - h)^2 + k, where (h, k) is the vertex. Identifying or constructing an equation for a parabola given its vertex involves plugging those coordinates into the formula.
Methods
Math Tutor Explanation Using Vertex Form
The vertex form of a parabola allows you to write the equation so the vertex is explicit.
Step 1: Step 1: Recall the vertex form of a quadratic equation: y = a(x - h)^2 + k
Step 2: Step 2: Substitute h = -3 and k = 2 into the formula
Math Tutor Explanation Using Completing the Square
Given a general quadratic, completing the square transforms it into vertex form, revealing the vertex location.
Step 1: Step 1: Start with a quadratic like y = ax^2 + bx + c
Step 2: Step 2: Complete the square to rewrite it as y = a(x - h)^2 + k, where h and k are related to the vertex
Step 1:
Step 2:
Math Tutor suggests: Practice with Quadratic Vertices and Vertex Form
Explore more problems involving the vertex form of quadratic equations and identifying vertices on graphs to strengthen your understanding.
FAQ on Parabola Vertex Form
What is the vertex form of a quadratic equation?
The vertex form is y = a(x - h)^2 + k, where (h, k) is the vertex.
How do you find the vertex from standard form?
Find h = -b/(2a) and k by substituting h back into the equation.
Can the value of 'a' be any number?
Yes, 'a' can be any nonzero real number. It determines the parabola's width and the direction it opens.
Why does (x + 3) indicate the vertex is at x = -3?
Because vertex form uses (x - h); setting h = -3 means the formula is (x - (-3)) = (x + 3).