How to Teach Long Division: Tips and Techniques
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on January 20, 2026
If your kid hasn’t figured out a working long division method, learning math together can turn into a minefield. But don’t worry, with this handy how-to guide, you’ll explore how to teach long division and help your child overcome the most common long division problems.
Key points
- While in some countries, long division problems are simplified or delayed, it is still taught in 4th grade in the US.
- The best way to teach long division is to connect it with already gained knowledge to explain its logic and use real-life examples.
- The Brighterly math and reading platform uses interactive methods to teach mathematics and long division specifically.
- To teach long division to grade 3 kids, use all the possible means for visualization, don’t require speed and accuracy, and use one-digit dividends only. These students need more attention and a more thoughtful explanation of long division.
- 4th grade students are already expected to deal with multiplication facts faster and have no problems with remembering the sequence “divide, multiply, subtract, bring down.”
- In 5th grade, it’s worth concentrating on teaching kids to estimate long division problems and increase their autonomy to find the right tool to deal with them.
At what grade do you learn long division?
Teaching long division is usually introduced in the 4th grade. However, students first approach division in the 2nd and 3rd grade, gradually progressing from short division with remainders to long division in 4th grade.
Note: Some modern curricula may delay or simplify long division and focus more on conceptual understanding, mental strategies, and models. In the US, long division is formally taught in 4th grade, though.
How to teach kids long division for the first time
You can use different ways to teach long division, but the main idea is to clarify its logic so they understand how and why they need it. At a glance, the long division method seems too hard, so the initial task is to make this method look less scary and connect it with already gained knowledge to explain its logic.
If you struggle with explaining long division, online educational resources like Brighterly math and reading platform often use interactive ways to introduce and improve long division understanding.
For example, math tutors use realistic examples, ideally linked to problems children may encounter. They describe some real-life dilemmas, like making a cupcake with a big cake recipe or distributing tickets to the same music concert between cities on tour to show when people typically engage in a long division process — and when a calculator doesn’t work alone.
Once tutors and kids reach an understanding of why they need it, the long division strategy is so much simpler to grasp.
The Brighterly math program for 1–9 grades is what many kids relate to: blending interactivity with fun examples and standard curriculum, so math classes at home match education in school. This is a very useful approach that many parents can adapt for their own tutoring.
Teaching how to divide step by step
- Detect the need to use long division methods
- Make your first division steps
- Get your first results
- Continue dividing until you get a final result
Step 1. Detect the need to use long division methods
Make it clear that the division requires (1) a divisor, (2) a dividend, and (3) a separation between them that comes as a right parenthesis [ ) ] or a vertical bar [ | ].
What to do if there is a problem here? “Divisor” and “dividend” may cause confusion because these words start with the same four letters. In this case, be creative! For example, you can use mnemonic devices to help kids learn these terms. Ideally, they should end with “-sor” and “-dend” and have active/passive analogies.
Example: You can refer to words like “professor” and “student” or “sponsor” and “respondent” to show the difference.
Step 2. Make your first division steps
The next step in the long division steps is to find the first digit of the divisor. Then, look at your dividend. Try to divide these two digits and write down the result you get separately.
What to do if there is a problem here? It may happen that the first digit of a divisor is smaller than the dividend. In this case, just use the first two digits of a divisor and write down your result.
Example: You have to divide 146 by 2. In this example, 1 is less than 2, so you should use 14 as a divisor, divide it by 2, and get 7 as the result.
Note: If you have to divide 147 by 21, you should use not 14 and 2 but 14 and 21.
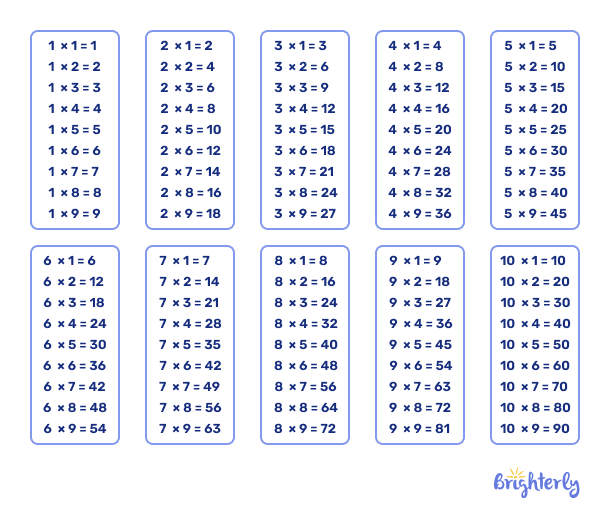
But it may happen that the first digit of a divisor is not divisible by the first digit of a dividend. To see how to long divide, long division recommends to find the closest number less than your digit(s) to divide (you may need to refer to a multiplication table for reference), and write down the result.
Example: If you have to divide 143 by 21, the answer of 7 doesn’t work because it yields 147, not 143. In this case, you should use 6 as the closest answer to your task, multiply 21 by 6, and subtract 21 multiplied by 6 (21 * 6 = 126) from 143.
Step 3. Get your first results
Congratulations! Now it’s time to know that your result is the first digit in your answer and the result you’re looking for is titled “quotient.” Time to get to the next digit in your divisor, divide it by a dividend and get the second digit of your quotient as a result! Basically, repeating this operation helps practice long division for kids.
What to do if there is a problem here? If your digit was not divisible in the previous step, you will need to subtract the difference between the real digit(s) of a divisor and the number you’ve used to divide. Just add the next digit of your divisor to the subtraction result you’ve got.
Example: You had to divide 356 by 20. In step 2, you divided 35 by 20 and got 1 as the first digit in the quotient. In step 3, you’ve got 15 as a subtraction result of 35-20. In this scenario, your next steps in long division are to write the last digit of your divisor next to your subtraction result and divide it by your dividend. In this example, you get 156 and divide it by 20.
By the way, to practice any of these steps, I have a great selection of long division worksheets! You can start by clicking the link Long Division Worksheets Grade 3!
Step 4. Continue dividing until you get a final result
You can repeat steps 2 and 3 until you get your final result. If things go smoothly, you’ll unlock the answer pretty fast!
What to do if there is a problem here? It may happen that when you’ve run out of digits in a divisor, you still have some number left as a subtraction result. Worry not! Leave this number and memorize that it’s called “remainder.”
Example: In our example of dividing 356 by 20, you get the task to divide 156 by 20 as your last step. Since the closest number for the second digit in a quotient is 7, you get 17 as your quotient answer and 156-140=16 as your remainder.
|
13 → quotient 20 ) 356 ____ 156 |
Long division strategies
Note: Long division help for kids involves understanding which method works best for specific learning styles..
Standard algorithm
Best for: logical learning, kids who learn best with steps and a clear routine.
In the long division standard algorithm, you use the traditional procedure of dividing, multiplying, and subtracting described in our step-by-step guide above. In this strategy, your task is to get a quotient and a remainder and stop there. The standard algorithm is best used with traditional math worksheets.
Partial quotients
Best for: conceptual thinkers, students with math anxiety.
Frequently referred to as the most intuitive for teachers to explain long division, the long division strategy of partial quotients lets them break the division problem into smaller, manageable parts and estimate how many dividends fit into a divisor. This method works especially well if kids have learned how to multiply pretty well.
Example: If you need to divide 268 by 2, you start by estimating the quotient that can fit as an answer. If it’s clear that at least 100 groups of 2 will work, you write down 100 in the answer field and subtract 100 multiplied by 2 (100 * 2 = 200) from 268 to get 68.
You repeat the same operation with 68 and get 30 as your next partial quotient and 8 as a subtraction result (68 – 60 = 8). Finally, you get 4 as a final partial quotient (8 / 2 = 4), and calculate the final result as a sum of all quotient parts (100 + 30 + 4 = 134).
| 2 ) 268 – 200 ← 2 x 100 __ 68 – 60 ← 2 x 30 __ 8 – 8 ← 2 x 4 __ 0 |
Box method
Best for: visual learners, children with math anxiety.
The box method is a long division step by step for visual learners that introduces an easy-to-follow box structure for all the mathematical operations done. Basically, the procedure is similar to the partial quotients method but the graphic presentation is linear.
| 100 + 30 + 4 = 134 _____________ 2 | 268 | 68 | 8 | | – 200 | – 60 | – 8 | | 68| 8 | 0 | |
Mnemonic devices
Best for: auditory learners, kids with strong verbal memory.
If kids struggle with remembering the sequence of long division actions, you can introduce some helpful words, sentences or poems to help them remember — just like I’ve offered with the “professor”/”student” example.
In this case, you need to invent words that will start with “d” (for “divide”) and then go to “m” (for ”multiply”), “s” (for “subtract”) and “b” (for “bring down”). The easiest mnemonic device to remember “divide, multiply, subtract, bring down” is “dad, mother, sister, brother.” Another great phrase is, “Does McDonald’s Sell Cheeseburgers?”.
How to teach long division to struggling students
If you still don’t know how to explain long division to a child, there is a need to combine several strategies and adjust them to their individual needs. We’ll discover some of your options below.

How to explain long division to struggling students: 5 tips
- Normalize mistakes
- Visualize the long division process
- Turn learning into a game
- Find helpful tools
- Practice, repeat, and track progress
Normalize mistakes
It’s hard to be patient, seeing your child make the same mistake over and over when you’re trying to figure out how to teach long division. But that’s critical to let them learn as long as they need, even if it means finding different ways to explain the same thing until they get it. With struggling students, it’s better to concentrate on progress, not perfection.
Visualize the long division process
Math is an abstract science, but a hands-on approach makes it more understandable for kids. Use the box method or real objects like apples and flowers to illustrate the logic and relationships between multiplication, division, and subtraction.
Turn learning into a game
You can make your math class more entertaining by introducing challenges into the long division studying process. It can be dividing as many digits as possible or solving a complicated long division task as a team.
Find helpful tools
One of the long division tricks is to introduce work mats, organizers, visual aids, and technology whenever you see kids struggling with a specific step in the long division process. The more angles they see and the more tools they have, the higher the chances your students get your long division explanation.
Practice, repeat, and track progress
The best way to teach long division is to turn it into an ongoing process. Like any other skill, long division needs constant practice, even when learned. Thus, keep your students practicing and encourage their progress with rewards.
How to do long division estimation?
Long division estimation means finding a reasonable answer by rounding numbers to ones that are easy to divide so you divide the rounded numbers mentally to check whether the answer makes sense.
How do you do long division estimation? Here are some steps to long division to help kids estimate long division problems, or apply the long division methods to the solution they want to get. And, if you need more info on division, you can find it in the article How to Teach Kids Division?
1. Partial quotients
In this method, you start by determining the final result as a solution in Step 1. For this, you find partial quotients or break down the problem into smaller steps that eventually bring you to the desired outcome.
2. Box method
While referring to the box method to how to do long division step by step, kids determine their long division problem as a lack of visualization for an abstract math operation. In this case, boxes help them track the relationship between multiplication and division and get the quotient.
3. Hands-on approach
Going for a hands-on approach is the next step in getting long division explained and getting a better understanding of its logic. By using blocks in class, you provide kids with a model to solve long division problems that explains what happens with a divisor and a dividend on the way.
4. Real-world examples
Whenever facing frustration, search for real-world examples to introduce familiar concepts that can explain long division activities. You can refer to sharing snacks, dividing pages in a book or estimating the cost of groceries for this. The closer your object is to the class, the better.
5. Long division worksheets
Long division problems may appear long after its logic is learned, and practice and repetition are a solution to them. In this regard, Long Division Worksheets are the best tool to refresh the long division skills, regain confidence, and make progress.
How to teach long division to grade 3
When do kids learn long division? As early as 3rd grade!
To teach long division to grade 3 kids, use all the possible means for visualization, don’t require speed and accuracy, and use one-digit dividends only. These students need more attention and a more thoughtful explanation of long division.
Long division 3rd grade steps
- Explain the concept
- Practice division and multiplication facts
- Show the box method
- Use mnemonic devices
- Provide practice and feedback
1. Explain the concept
To show how does long division work to a 3rd grader, use real-world facts and take enough time to explain the logic behind long division
2. Practice division and multiplication facts
Step by step long division for 3rd graders involves applying flashcards, tests, and games to remind multiplication and division facts.
3. Show the box method
The box method is the best approach to use for grade 3 students because it helps to visualize the process of multiplication and division and track the long division more easily.
4. Use mnemonic devices
Mnemonic devices are another useful long division method that helps with remembering the steps.
5. Provide practice and feedback
How to do long division for kids? Let grade 3 students practice long division at home and track their progress in class, increasing the difficulty of the tasks given gradually.
How to teach long division to grade 4
Regarding grade 4 long division steps, 4th grade students are already expected to deal with multiplication facts faster and have no problems with remembering the sequence “divide, multiply, subtract, bring down.” Thus, you can proceed to master the long division standard algorithm to improve efficiency and speed.
How to teach to grade 4 long division steps
- Review the long division skills
- Show different long division strategies
- Steadily increase the difficulty of long division tasks
- Repeat and practice
1. Review the long division skills
Warm up by determining the concept of long division, division and multiplication facts, and the steps in the process.
2. Show different long division strategies
Long division for 4th grade involves resolving the same tasks with different strategies to detect the one that works best for the students.
3. Steadily increase the difficulty of long division tasks
Aim at increasing the complexity yet encourage peer-to-peer learning and introduce helpful tools whenever needed.
4. Repeat and practice
Use long division worksheets for grade 4 to practice working with 4-digit divisors and ensure constant learning and practicing the skill.
If you need 4th grade long division practice right away, check out link Long Division Worksheets Grade 4!
How to teach long division to grade 5
Long division grade 5 step-by-step guide depends on the progress of the class in grade 3 and grade 4.
Ideally, it’s time to proceed to deal with 5-digit divisors and 2-digit dividends, but the exact teaching method will depend on the learning capabilities of the students. In any case, it’s worth concentrating on teaching kids to estimate long division problems and increase their autonomy to find the right tool to deal with them. These are the core long division strategies 5th grade.
5th grade long division steps for teaching
- Review long division skills
- Let students choose their long division strategy
- Steadily increase the difficulty of long division tasks
- Repeat and practice
1. Review long division skills
Check the progress and complexity of the class, refresh the knowledge and skills if needed.
2. Let students choose their long division strategy
Focus on long division problem estimation in determining the best long division strategy.
3. Steadily increase the difficulty of long division tasks
Steadily increase the number of digits in divisors and dividends and check if speed and efficiency issues appear. Long division grade 5 step by step is all about that.
4. Repeat and practice
If possible, design an individual plan for each student, considering their long division problems and areas for improvement. Using long division worksheets is useful at this stage.
If you need more diverse materials to practice, check out Long Division Worksheets Grade 5 with numerous examples.
Why do kids struggle with long division?
Kids struggle with long division because this requires multiple skills at the same time. This may overload working memory and cause confusion in most cases. The confusing long division tutorial they get in school doesn’t help the situation.
What are common mistakes in long division?
The most common mistakes in long division are forgetting to bring down the next digit, multiplication or subtraction errors, placing digits in the wrong place value, and ignoring remainders. Unfortunately, this happens quite often with kids.
For multiplication errors, you can check out this article – How to Teach Multiplication.
Conclusion
Teaching long division is not easy, but manageable with the right approach and by applying different long division strategies and closing knowledge gaps beforehand. For once, math tests are an awesome thing to catch those learning gaps early.
That’s why I recommend applying different long division worksheets, visualization means, strategies, and individual sessions with a math tutor whenever needed. Brighterly can help with this and many other math problems your kids may encounter — just book free math lesson!



















