Coordinate Plane – Definition with Examples
reviewed by Jo-ann Caballes
Updated on February 8, 2026
Welcome to Brighterly, where we make even the most seemingly difficult math concepts easy to understand and fun to learn.
Today, we’re going to cover the coordinate plane, which is an essential element of geometry and graphing. Here, we’ll cover the definition of the coordinate plane, how many number lines it has, and its individual elements. We’ll also give you some solved math tasks, practice problems, and cool worksheets so you can practice your knowledge.
What is a coordinate plane?
A coordinate plane is formed by a 2D (two-dimensional) grid that contains four quadrants and an x-axis and a y-axis. The coordinate plane is a key tool when it comes to visualizing locations and graphing data or points, lines, and shapes. We cover the full definition of the coordinate plane below.
Coordinate plane definition
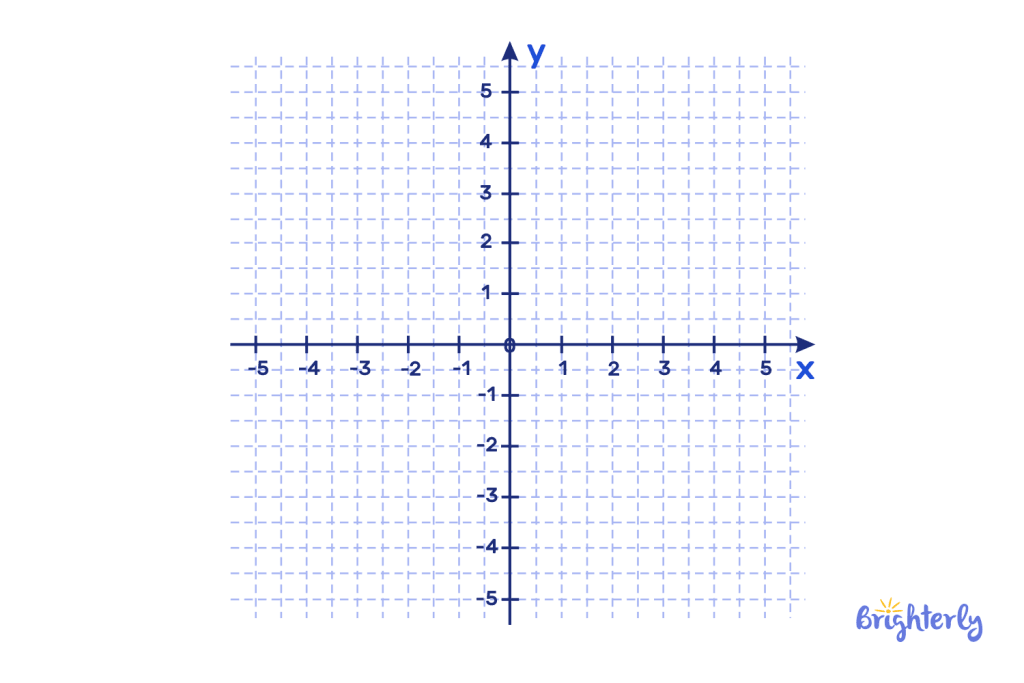
The definition of coordinate plane is a diagram that represents numbers as points on a plane. Two lines intersect perpendicularly to create four right angles and thus, four quadrants. The horizontal number line is the x-axis, and the vertical number line is the y-axis.
The coordinate plane is used to plot lines, graphs, and shapes, and any point that is plotted on a coordinate plane will have a location both on the x-axis and the y-axis.
The horizontal number line in the left quadrants will be represented by negative numbers (aka minus numbers), while the horizontal number line in the right quadrants will be represented by positive numbers. Conversely, the vertical number line in the lower quadrants will be represented by negative numbers, and the vertical number line in the upper two quadrants will be represented by positive numbers.
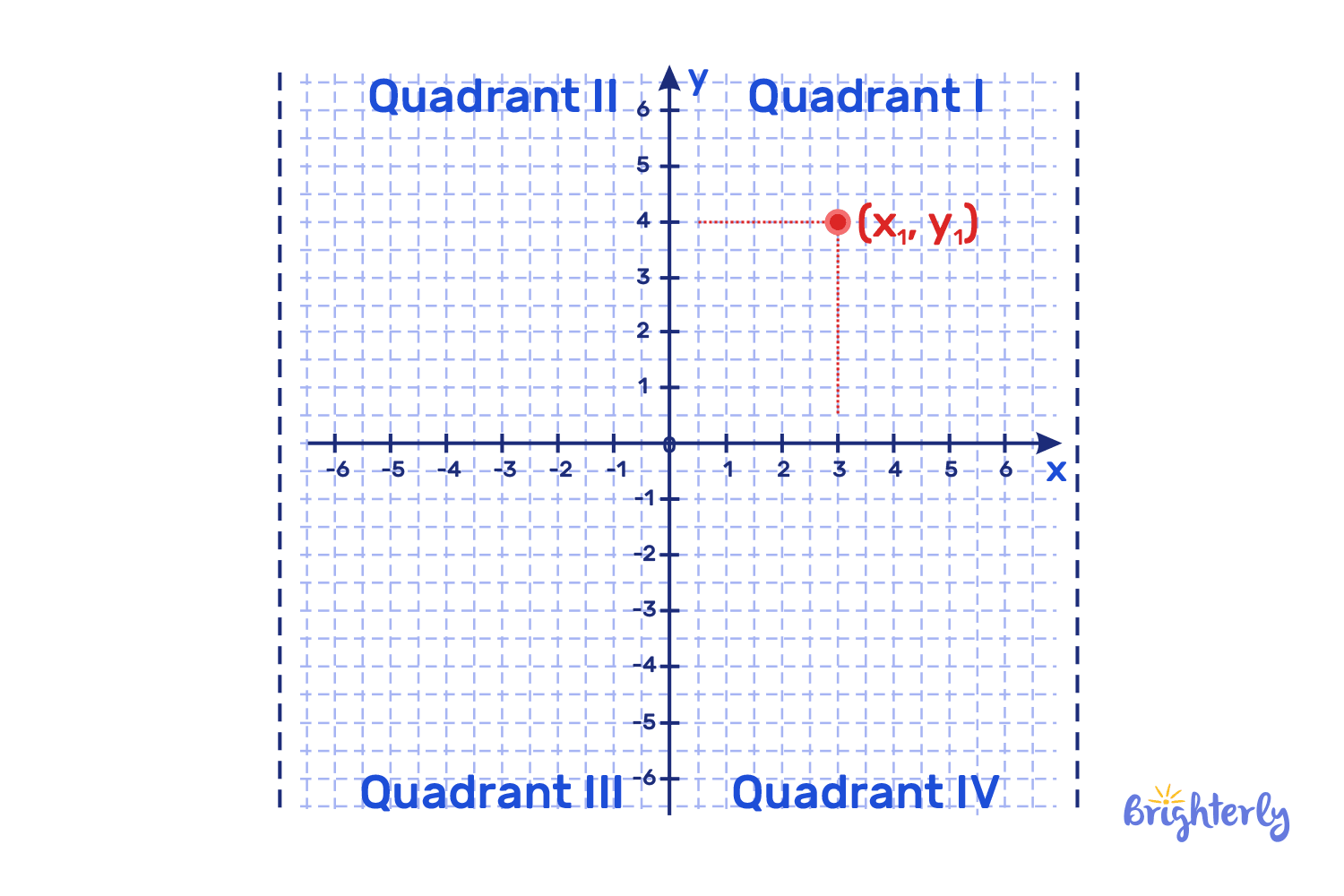
Coordinate plane quadrants
It’s important to be able to understand and identify each of your 4 coordinate planes’ quadrants:
- The first quadrant in the top right-hand corner is called the positive coordinates quadrant because all points here are positive (+, +). It is represented by I (the Roman numeral for 1)
- The second quadrant, in the top left-hand corner, has negative x-axis numbers and positive y-axis numbers (-, +). It is represented by II (the Roman numeral for 2)
- The third quadrant, in the bottom left-hand corner, has both negative x-axis and y-axis numbers (-, -) and is represented by III (the Roman numeral for 3)
- The fourth and final quadrant, in the bottom right-hand corner, has positive x-axis numbers and negative y-axis numbers (+, -) and is represented by the IV (the Roman numeral for 4)
What are the quadrants on a coordinate plane?
The quadrants are the four distinct regions created when the x-axis and y-axis intersect at the origin. You can think of them as four “neighborhoods” that help organize where points live based on whether their coordinates are positive or negative. Each quadrant is numbered I through IV in a counter-clockwise direction, starting from the top-right, which provides a clear map for any point your child needs to plot on the coordinates plane.
How many quadrants are in a coordinate plane?
There are exactly four quadrants in a standard coordinate plane, no more, no less! Because our two number lines (the horizontal x-axis and the vertical y-axis) meet at a perfect 90° angle, they separate the flat surface into four equal sections. Whether your kid is working with simple shapes or complex graphs, every point on the plane, unless it sits directly on an axis, will fall into one of these four specific sections.
Which two dimensions does a coordinate plane have?
The coordinate plane has two dimensions: horizontal (x) and vertical (y). This means it has no thickness or depth.
How many number lines does a coordinate plane have?
A coordinate plane has two number lines. It has one horizontal number line that stretches from left to right, and one vertical number line that stretches from top to bottom. These number lines are what divide the coordinate plane into four quadrants, as they intersect at the middle point of each line.
How to plot points on a coordinate plane?
It’s super easy to plot your points on your x, y coordinate plane. If you’re given a coordinate (or ordered pairs), for example, (3, -4), all you need to do is:
- Move the corresponding number of points along your x-axis first – here, you’d move 3 points along to the right
- Then, move the corresponding number of points up or down your y-axis – here, you’d move 4 points down
- Then, you simply mark your point! You can do this via a dot or with an X – your mark on the coordinate plane describes the location of a point
Coordinate plane elements
There are some key elements that all coordinate planes will have. The parts of a coordinate plane are:
- Two axes: an x-axis (horizontal) and a y-axis (vertical)
- Four quadrants
- The origin, which is the point at which the two number lines meet
- Number lines, which cover coordinate plane positive and negative numbers
- Coordinates, also known as ordered pairs, which state the location of a point on a graph – they represent the number the point represents on both axes
Coordinate plane example
When it comes to coordinate planes, it’s just as important to show as it is to tell!
Here is an example of a coordinate plane:

You’ll see all of our elements represented on this coordinate plane:
- Two number lines, which are placed vertically and horizontally and intersect at their middle points
- Four quadrants
- Gridlines, which allow us to easily plot our points on our coordinate plane
- You’ll also see some example points mapped out on the coordinate plane and their coordinates (ordered pairs)
- The points we plot out on a coordinate plane can be represented by their coordinate pairs – i.e. their corresponding points on both the x-axis and y-axis. In a coordinate pair, the x-axis point is always represented first. For example, (3, 4) would represent a point on the graph that is 3 spaces along and 4 spaces up.
How to read a coordinate plane
To read coordinate planes, you need to understand how to interpret the relationship between a point and its distance from the axes. To find the “address” of a specific point, you need to always start at the origin (0,0). Then, you look at the horizontal displacement first. By looking directly below or above the point to the x-axis, you identify the x-coordinate, which represents the horizontal “run.” Then, you look across the y-axis to find the y-coordinate, which represents the vertical “rise.” You then write both numbers as an ordered pair in the (x, y) format, and this will be the mathematical address of your point on a coordinate plane.
How to draw a coordinate plane
Drawing a coordinate plane graph begins with the precise interaction of two perpendicular lines. To draw them, use a straightedge and draw a horizontal line first, which will be your x-axis. Then, draw a vertical line, the y-axis, making sure that it intersects at a central point, known as the origin. Mark the axes as x and y, respectively. After this, mark equal intervals along each line to create a consistent scale, where the positive integers are located right and upward, and negative integers are on the left and downward.
Solved math tasks: examples
Are you ready to start working with coordinate planes in real life? Try out our solved math tasks and draw your own coordinate planes, then check our answers to see if you’ve got them right!
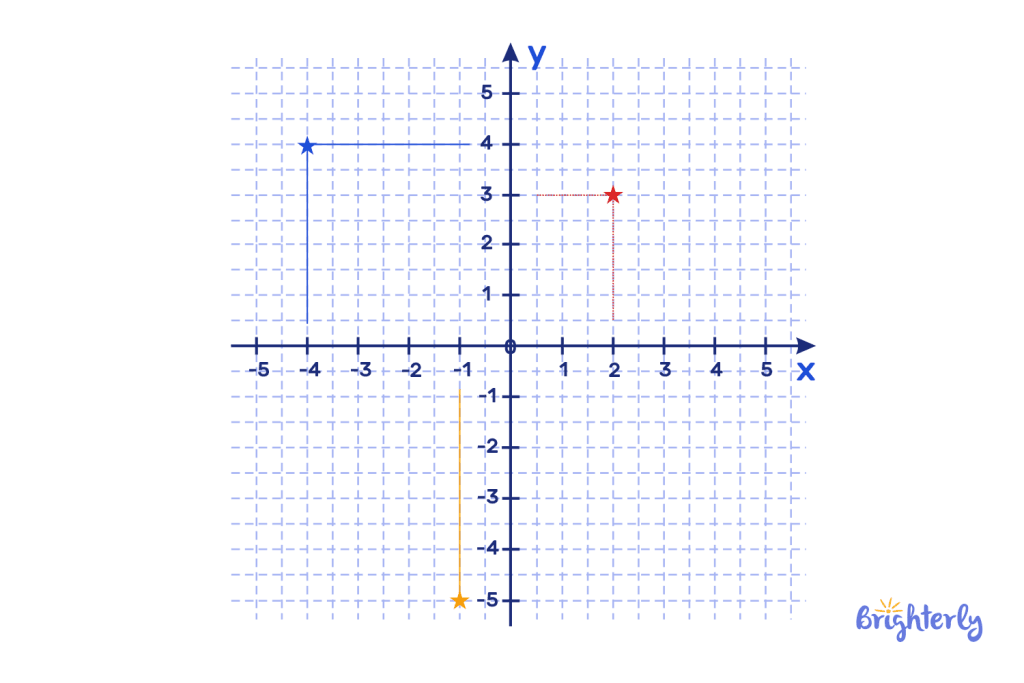
Solved math task 1
On the following coordinate plane, plot the following points:
- (2, 3)
- (-4, 4)
- (-1, -5)
Answer:
Your coordinate plane should be something like this:
Solved math task 2
Identify the ordering pairs (coordinates) of the points on the coordinate plane below:
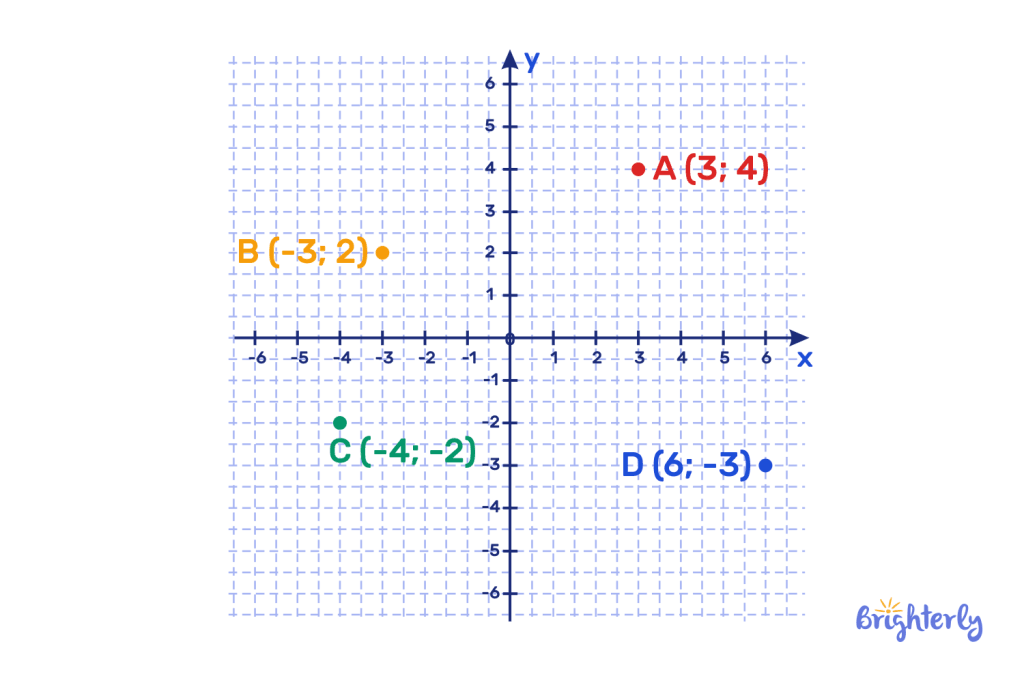
Answer:
The following coordinates are plotted on this coordinate plane:
|
Solved math task 3
Identify the ordering pairs (coordinates) of the points on the coordinate plane below:
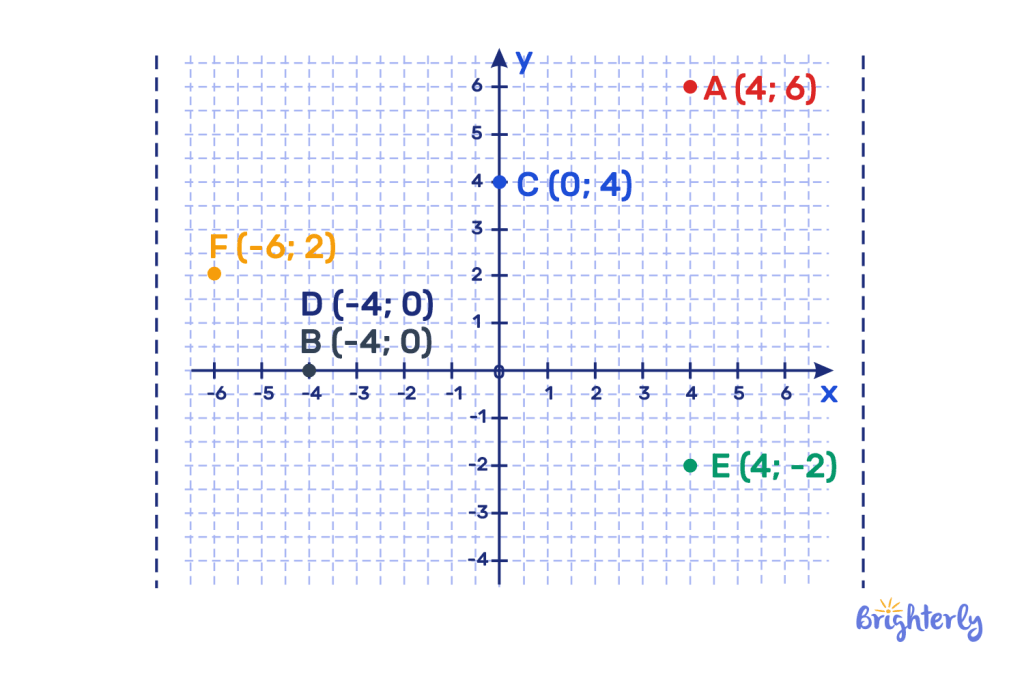
Answer:
The following coordinates are plotted on this coordinate plane:
|
Coordinate plane: practice math problems
Coordinate plane worksheets
Now that you know the coordinate plane definition in math and how to plot your points, are you ready to carry out more work with coordinate planes? Download our fun, free math worksheets to put your knowledge to the test and become a master of working with coordinate planes!